The spoils of war and the long-term spoiling of health conditions of entire nations
- PMID: 35644760
- PMCID: PMC9122842
- DOI: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2022.05.012
The spoils of war and the long-term spoiling of health conditions of entire nations
Abstract
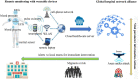
The healthcare system of Ukraine was already suffering from several shortfalls before February 2022, but the war of aggression started by the Russian leadership is poised to inflict a further severe blow that will have long-lasting consequences for the health of all Ukrainians. In pre-war Ukraine, noncommunicable diseases (NCDs) contributed to 91% of deaths, especially cardiovascular diseases (67%). Ukrainians have a high prevalence of risk factors for NCDs ranking among the highest levels reported by the World Health Organization (WHO) in the European (EU) Region. Cardiovascular disease is one of the key health risks for the conflict-affected Ukrainian population due to significant limitations in access to health care and interruptions in the supply of medicines and resources. The excess mortality observed during the COVID-19 pandemic, due to a combination of viral illness and chronic disease states, is bound to increase exponentially from poorly treated NCDs. In this report, we discuss the impact of the war on the public health of Ukraine and potential interventions to provide remote health assistance to the Ukrainian population.
Keywords: Cardiovascular disease; Healthcare systems; Remote monitoring; Ukraine; War.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Reply to: "The spoils of war and the long-term spoiling of health conditions of entire nations".Atherosclerosis. 2022 Aug;355:83. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2022.07.001. Epub 2022 Jul 14. Atherosclerosis. 2022. PMID: 35871856 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Ukraine refugee situation. Operational data portal. https://data2.unhcr.org/en/situations/ukraine
-
- World Health Organization Surveillance system for attacks on health care (SSA) https://extranet.who.int/ssa/Index.aspx
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control . 2022. Operational Considerations for the Prevention and Control of Infectious Diseases - Russia's Aggression towards Ukraine.
-
- World Health Organization World Tuberculosis Day: supporting Ukraine in scaling up TB diagnosis and treatment. https://www.euro.who.int/en/countries/ukraine/news/news/2021/3/world-tub...
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control . 2019. HIV/AIDS Surveillance in Europe 2021 – 2020 Data.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

