Association between hyperglycaemia in pregnancy and growth of offspring in early childhood: The PANDORA study
- PMID: 35644889
- PMCID: PMC9539556
- DOI: 10.1111/ijpo.12932
Association between hyperglycaemia in pregnancy and growth of offspring in early childhood: The PANDORA study
Abstract
Background: Few studies have assessed whether children exposed to in utero hyperglycaemia experience different growth trajectories compared to unexposed children.
Objectives: To assess association of type 2 diabetes (T2D) and gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) with early childhood weight, length/height and body mass index (BMI) trajectories, and with timing and magnitude of peak BMI in infancy.
Methods: PANDORA is a birth cohort recruited from an Australian hyperglycaemia in pregnancy register, and women with normoglycaemia recruited from the community. Offspring growth measures were obtained from health records over a median follow-up of 3.0 years (interquartile range 1.9-4.0). This analysis included children born to Aboriginal mothers with in utero normoglycaemia (n = 95), GDM (n = 228) or T2D (n = 131). Growth trajectories (weight, length/height and BMI) were estimated using linear mixed models with cubic spline functions of child age.
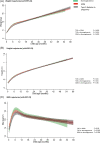
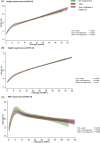
Results: After adjustment for maternal factors (age, BMI, parity, smoking, and socioeconomic measures) and child factors (age, gestational age at birth, and sex), children born to mothers with T2D or GDM had lower weight, length/height and BMI trajectories in infancy than children born to mothers with normoglycaemia, but similar weight and BMI by completion of follow-up. Children exposed to T2D had lower mean peak BMI 17.6 kg/m2 (95% confidence interval [CI] 17.3-18.0) than children exposed to normoglycaemia (18.6 kg/m2 [18.1-18.9]) (p = 0.001).
Conclusions: Maternal hyperglycaemia was associated with differences in early childhood growth trajectories after adjustment for maternal BMI. Exploration of associations between in utero hyperglycaemia exposure and growth trajectories into later childhood is required.
Keywords: Aboriginal; child; diabetes; growth; pregnancy.
© 2022 The Authors. Pediatric Obesity published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of World Obesity Federation.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflict of interest was declared.
Figures

References
-
- WHO Multicentre Growth Reference Study Group . WHO Child Growth Standards: Methods and Development. World Health Organization; 2006.
-
- Baur LA, Garnett SP. Early childhood—a critical period for obesity prevention. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2019;15(1):5‐6. - PubMed
-
- Geserick M, Vogel M, Gausche R, et al. Acceleration of BMI in early childhood and risk of sustained obesity. N Engl J Med. 2018;379(14):1303‐1312. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

