Simple, accurate calculation of mechanical power in pressure controlled ventilation (PCV)
- PMID: 35644896
- PMCID: PMC9148680
- DOI: 10.1186/s40635-022-00448-5
Simple, accurate calculation of mechanical power in pressure controlled ventilation (PCV)
Abstract
Background: Mechanical power is a promising new metric to assess energy transfer from a mechanical ventilator to a patient, which combines the contributions of multiple parameters into a single comprehensive value. However, at present, most ventilators are not capable of calculating mechanical power automatically, so there is a need for a simple equation that can be used to estimate this parameter at the bedside. For volume-controlled ventilation (VCV), excellent equations exist for calculating power from basic ventilator parameters, but for pressure-controlled ventilation (PCV), an accurate, easy-to-use equation has been elusive.
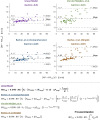
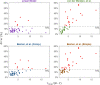
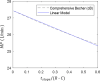
Results: Here, we present a new power equation and evaluate its accuracy compared to the three published PCV power equations. When applied to a sample of 50 patients on PCV with a non-zero rise time, we found that our equation estimated power within an average of 8.4% ± 5.9% (mean ± standard deviation) of the value obtained by numerical integration of the P-V loop. The other three equations estimated power with an error of 19.4% ± 12.9% (simplified Becher equation), 10.0% ± 6.8% (comprehensive Becher equation), and 16.5% ± 14.6% (van der Meijden equation).
Conclusions: Our equation calculates power more accurately than the other three published equations, and is much easier to use than the only previously published equation with similar accuracy. The proposed new mechanical power equation is accurate and simple to use, making it an attractive option to estimate power in PCV cases at the bedside.
Keywords: Mechanical power equation; Mechanical ventilation; Pressure-controlled ventilation.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
None to declare.
Figures


References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

