Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Sensors for SARS-CoV-2: Where Are We Now?
- PMID: 35645185
- PMCID: PMC9149885
- DOI: 10.3390/biomimetics7020058
Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Sensors for SARS-CoV-2: Where Are We Now?
Abstract
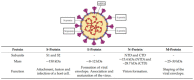
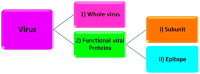
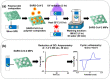
Since the first reported case of COVID-19 in 2019 in China and the official declaration from the World Health Organization in March 2021 as a pandemic, fast and accurate diagnosis of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has played a major role worldwide. For this reason, various methods have been developed, comprising reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), immunoassays, clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR), reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RT-LAMP), and bio(mimetic)sensors. Among the developed methods, RT-PCR is so far the gold standard. Herein, we give an overview of the MIP-based sensors utilized since the beginning of the pandemic.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; biomimetic sensors; molecularly imprinted polymers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
RT-LAMP CRISPR-Cas12/13-Based SARS-CoV-2 Detection Methods.Diagnostics (Basel). 2021 Sep 8;11(9):1646. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11091646. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34573987 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optimization of loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assay for robust visualization in SARS-CoV-2 and emerging variants diagnosis.Chem Eng Sci. 2022 Apr 6;251:117430. doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2022.117430. Epub 2022 Jan 13. Chem Eng Sci. 2022. PMID: 35043022 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in methods for the diagnosis of Corona Virus Disease 2019.J Clin Lab Anal. 2022 Jan;36(1):e24178. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24178. Epub 2021 Dec 17. J Clin Lab Anal. 2022. PMID: 34921443 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rapid, Sensitive, and Specific Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Detection: A Multicenter Comparison Between Standard Quantitative Reverse-Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction and CRISPR-Based DETECTR.J Infect Dis. 2021 Feb 3;223(2):206-213. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiaa641. J Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 33535237 Free PMC article.
-
Development and Clinical Application of a Rapid and Sensitive Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Test for SARS-CoV-2 Infection.mSphere. 2020 Aug 26;5(4):e00808-20. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00808-20. mSphere. 2020. PMID: 32848011 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Electrochemical and Bioelectrochemical Sensing Platforms for Diagnostics of COVID-19.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Mar 3;13(3):336. doi: 10.3390/bios13030336. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36979548 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Low-Cost Biosensor Technologies for Rapid Detection of COVID-19 and Future Pandemics.ACS Nano. 2024 Jan 23;18(3):1757-1777. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.3c01629. Epub 2024 Jan 8. ACS Nano. 2024. PMID: 38189684 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Imprinted Polymers on the Route to Plastibodies for Biomacromolecules (MIPs), Viruses (VIPs), and Cells (CIPs).Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 2024;187:107-148. doi: 10.1007/10_2023_234. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 37884758 Review.
References
-
- Abdalla M.S., Altintas Z., Forster R.J., Chemistry B., Industries B.P., St R.H., Abageyah A., Governorate C. Current Trends of SARS-CoV-2 and Its New Variants Diagnostics in Different Body Fluids: Surface Antigen, Antibody, Nucleic Acid, and RNA Sequencing Detection Techniques. [(accessed on 9 April 2022)]. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=4016299.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

