Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Sensors for SARS-CoV-2: Where Are We Now?
- PMID: 35645185
- PMCID: PMC9149885
- DOI: 10.3390/biomimetics7020058
Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Sensors for SARS-CoV-2: Where Are We Now?
Abstract
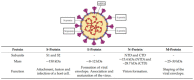
Since the first reported case of COVID-19 in 2019 in China and the official declaration from the World Health Organization in March 2021 as a pandemic, fast and accurate diagnosis of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has played a major role worldwide. For this reason, various methods have been developed, comprising reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), immunoassays, clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR), reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RT-LAMP), and bio(mimetic)sensors. Among the developed methods, RT-PCR is so far the gold standard. Herein, we give an overview of the MIP-based sensors utilized since the beginning of the pandemic.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; biomimetic sensors; molecularly imprinted polymers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Abdalla M.S., Altintas Z., Forster R.J., Chemistry B., Industries B.P., St R.H., Abageyah A., Governorate C. Current Trends of SARS-CoV-2 and Its New Variants Diagnostics in Different Body Fluids: Surface Antigen, Antibody, Nucleic Acid, and RNA Sequencing Detection Techniques. [(accessed on 9 April 2022)]. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=4016299.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

