Comparative Evaluation of the Efficacy of Virtual Reality Distraction, Audio Distraction and Tell-show-do Techniques in Reducing the Anxiety Level of Pediatric Dental Patients: An In Vivo Study
- PMID: 35645488
- PMCID: PMC9108792
- DOI: 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-2106
Comparative Evaluation of the Efficacy of Virtual Reality Distraction, Audio Distraction and Tell-show-do Techniques in Reducing the Anxiety Level of Pediatric Dental Patients: An In Vivo Study
Abstract
Objectives and methods: Children, in the age-group of 6 to 8 years, with moderate level of anxiety, (measured with M-DAS), requiring inferior alveolar nerve block (IANB) for mandibular tooth extraction were selected. Informed consent was obtained from parents. Selected children were allocated randomly into 3 groups virtual reality (VR) distraction group, audio distraction group and Tell-show-do (TSD) group. Pre- and post- distraction anxiety level of children was measured subjectively with facial image scale and objectively with pulse rate and oxygen saturation (measured with pulse oxymeter).
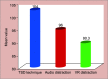
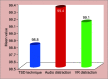
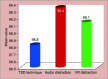
Results: There was a statistically significant decrease in pulse rate after distraction (with a p < 0.01) in all the three groups. Postdistraction pulse rate was lowest in the VR distraction group when compared to other groups. While comparing postdistraction pulse rate values in the three groups, the difference in pulse rate between TSD and VR distraction group was significant. But while comparing the pulse rate between audio distraction and TSD group (p = 0.06), and audio distraction and VR distraction group (p = 0.24) was not statistically significant. Oxygen saturation increased in all the three groups which was statistically significant (p < 0.01). There was a statistically significant difference in the postdistraction oxygen (O2) saturation levels between TSD and audio distraction groups (p < 0.05) with more O2 saturation in audio distraction group. But while comparing the audio distraction with VR group and TSD with VR group, the difference was not significant. Facial image scale (FIS) scores decreased in all the three groups (p < 0.01).
Conclusion: The overall results revealed by all the parameters indicate that children were most relaxed in VR group, followed by audio group and were least relaxed in TSD group during dental visits. Hence VR distraction can be considered as a useful technique for behavior management of pediatric patients during a conventional dental treatment.
How to cite this article: SG G, George S, S A, et al. Comparative Evaluation of the Efficacy of Virtual Reality Distraction, Audio Distraction and Tell-show-do Techniques in Reducing the Anxiety Level of Pediatric Dental Patients: An In Vivo Study. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent 2021;14(S-2):S173-S178.
Keywords: Nonpharmacological; Pain; Pain perception; Parental acceptance; Patient accept; Pediatric dental care; Pharmacological management; Tell-show-do (TSD).
Copyright © 2021; The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Source of support: Nil Conflict of interest: None
Figures

Similar articles
-
Evaluation of Effect of Distraction Techniques Using Virtual Reality and Eight-dimension Audio Analgesia Methods on Pain Perception and Anxiety Levels in Children During Restorative Procedures: A Comparative In Vivo Study.Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2024 Oct;17(10):1087-1092. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-2960. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2024. PMID: 39650306 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of Distraction with Virtual Reality Eyewear in Managing 6-11-year-old Children with Hearing Impairment during Dental Treatment: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2023 Nov-Dec;16(6):820-823. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-2588. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2023. PMID: 38344382 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Effectiveness of Audio and VR Distraction Techniques in Managing Pediatric Dental Patients.J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2024 Feb;16(Suppl 1):S504-S506. doi: 10.4103/jpbs.jpbs_831_23. Epub 2023 Nov 7. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2024. PMID: 38595406 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of Audio and Audio-Visual Distraction Aids for Management of Pain and Anxiety in Children and Adults Undergoing Dental Treatment- A Systematic Review And Meta-Analysis.J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2022 Mar 1;46(2):86-106. doi: 10.17796/1053-4625-46.2.2. J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2022. PMID: 35533223
-
The effect of audio distraction in reducing signs of stress and anxiety during pediatric dental treatment: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Oral Investig. 2025 Jan 13;29(1):58. doi: 10.1007/s00784-024-06035-0. Clin Oral Investig. 2025. PMID: 39804393
Cited by
-
Assessment of Different Distraction Behavioral Methods in Pediatric Dental Clinic: A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2023 Jul 24;15(7):e42366. doi: 10.7759/cureus.42366. eCollection 2023 Jul. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37621781 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of Effect of Distraction Techniques Using Virtual Reality and Eight-dimension Audio Analgesia Methods on Pain Perception and Anxiety Levels in Children During Restorative Procedures: A Comparative In Vivo Study.Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2024 Oct;17(10):1087-1092. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-2960. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2024. PMID: 39650306 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Evaluation of Reframing and Tell-show-do Behavior Guidance Technique in the Management of Dental Anxiety among Children Aged 6-12 Years Undergoing Dental Treatment without and with Administration of Local Anesthesia: A Single-Blind Randomized Clinical Study.Contemp Clin Dent. 2025 Apr-Jun;16(2):81-86. doi: 10.4103/ccd.ccd_35_25. Epub 2025 Jul 14. Contemp Clin Dent. 2025. PMID: 40799221 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review and network meta-analysis of virtual reality, audiovisuals and music interventions for reducing dental anxiety related to tooth extraction.BMC Oral Health. 2023 Sep 22;23(1):684. doi: 10.1186/s12903-023-03407-y. BMC Oral Health. 2023. PMID: 37735362 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Evaluation of Behavioral and Physiological Outcomes on Dental Anxiety of Children Undergoing Dental Treatment: A Randomized Clinical Trial.Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2025 Apr;18(4):383-393. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-3088. Epub 2025 May 19. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2025. PMID: 40469821 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aitken JC, Wilson S, Coury D, et al. The effect of music distraction on pain, anxiety and behaviour in Pediatric dental patients. Pediatric Dent. 2002;24(02):114–118. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
