The Inflammation in the Cytopathology of Patients With Mucopolysaccharidoses- Immunomodulatory Drugs as an Approach to Therapy
- PMID: 35645812
- PMCID: PMC9136158
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.863667
The Inflammation in the Cytopathology of Patients With Mucopolysaccharidoses- Immunomodulatory Drugs as an Approach to Therapy
Abstract
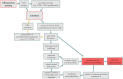
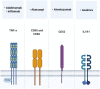
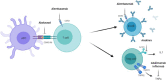
Mucopolysaccharidoses (MPS) are a group of lysosomal storage diseases (LSDs), characterized by the accumulation of glycosaminoglycans (GAGs). GAG storage-induced inflammatory processes are a driver of cytopathology in MPS and pharmacological immunomodulation can bring improvements in brain, cartilage and bone pathology in rodent models. This manuscript reviews current knowledge with regard to inflammation in MPS patients and provides hypotheses for the therapeutic use of immunomodulators in MPS. Thus, we aim to set the foundation for a rational repurposing of the discussed molecules to minimize the clinical unmet needs still remaining despite enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT).
Keywords: MPS; cytopathology; drug discovery; immunomodulation; inflammation; mucopolysaccharidoses.
Copyright © 2022 Wiesinger, Bigger, Giugliani, Scarpa, Moser, Lampe, Kampmann and Lagler.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ahmed A., Whitley C. B., Cooksley R., Rudser K., Cagle S., Ali N., et al. (2014). Neurocognitive and Neuropsychiatric Phenotypes Associated with the Mutation L238Q of the α-L-iduronidase Gene in Hurler-Scheie Syndrome. Mol. Genet. Metab. 111, 123–127. 10.1016/j.ymgme.2013.11.014 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

