Recruitment Traits Could Influence Species' Geographical Range: A Case Study in the Genus Saxifraga L
- PMID: 35646004
- PMCID: PMC9136331
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2022.827330
Recruitment Traits Could Influence Species' Geographical Range: A Case Study in the Genus Saxifraga L
Abstract
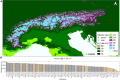
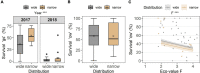
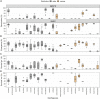
The reasons why some species occur widespread, while related species have restricted geographical ranges have been attributed to habitat specialization or ecological niche breadth. For species in the genus Saxifraga, habitat specialization alone cannot explain the distributional differences observed. We hypothesize that recruitment traits (i.e., germination, emergence, and survival) may account for differences in geographical ranges and that early life stages correlate to survival. We studied recruitment responses in 13 widespread and 12 narrow-ranged Saxifraga species in the laboratory and common garden experiments using seeds collected from 79 populations in the European Alps. We found that in the laboratory cold temperature led to higher germination percentages compared with warm temperature for both distribution groups. This represents an exception to the general assumption that alpine species require warm cues for germination. In warm laboratory temperatures, widespread species germinated better than narrow-ranged species, indicating a greater tolerance of warm temperatures for the former. Subsequent to germination, recruitment traits between the two distribution groups were lower or null in the common garden, suggesting that the impact of recruitment on species' geographical ranges occurs at the earliest life stage. Mean time to emergence of narrow-ranged species showed lower variability than that of widespread species. Consistently, intraspecific variation of mean annual temperatures between seed collection sites was lower for narrow-ranged species, indicating a close relationship between home sites and emergence time. Emergence percentage was a strong predictor of survival only for widespread species, underlining that seed and seedling functional traits differ between distribution groups, which require further research. Our results support the view that early life stages are critical to population dynamics and thus can influence species' geographical ranges. The wider responses to climatic conditions in widespread species may have facilitated their spread across the Alps. Our results also suggest that all Saxifraga species face a considerable threat from climate warming due to their overall cold-adapted recruitment niche.
Keywords: common garden; germination; intraspecific variation; phenology; regeneration niche; seed sowing experiment.
Copyright © 2022 Margreiter, Porro, Mondoni and Erschbamer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Aeschimann D., Lauber K., Moser D. M., Theurillat J.-P. (2004). Flora alpina. Bern: Haupt Berne.
-
- Albert C. H., Thuiller W., Yoccoz N. G., Soudant A., Boucher F., Saccone P., et al. (2010b). Intraspecific functional variability: extent, structure and sources of variation. J. Ecol. 98 604–613. 10.1111/j.1365-2745.2010.01651.x - DOI
-
- Albert C. H., Thuiller W., Yoccoz N. G., Douzet R., Aubert S., Lavorel S. (2010a). A multi-trait approach reveals the structure and the relative importance of intra- vs. interspecific variability in plant traits. Funct. Ecol. 24 1192–1201. 10.1111/j.1365-2435.2010.01727.x - DOI
-
- Ascough G. D., Erwin J. E., Van Staden J. (2007). Temperature-dependent seed germination in Watsonia species related to geographic distribution. S. Afr. J. Bot. 73 650–653. 10.1016/j.sajb.2007.05.004 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

