Molecular Mechanism of the Effect of Zhizhu Pill on Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking
- PMID: 35646148
- PMCID: PMC9135531
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/2996865
Molecular Mechanism of the Effect of Zhizhu Pill on Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking
Abstract
Background: To investigate the pharmacological mechanism of Zhizhu pill (ZZP) against gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), network pharmacology in combination with molecular docking was applied in this study.
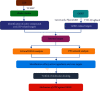
Methods: Active compounds of ZZP and target genes related to GERD were identified through public databases. Subsequently, the obtained data were used as a basis for further network pharmacological analysis to explore the potential key active compounds, core targets, and biological processes involved in ZZP against GERD. Finally, the results predicted by network pharmacology were validated by molecular docking.
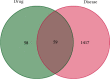
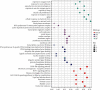
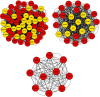
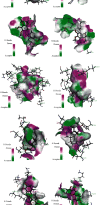
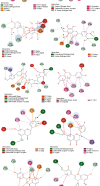
Results: Twenty active components of ZZP were identified to act on 59 targets related to GERD. Enrichment analysis revealed that multiple biological processes including response to oxygen levels, response to oxidative stress, and response to reactive oxygen species were involved in the GERD ZZP treatment with ZZP. ZZP had an impact on the prognosis of GERD mainly through the HIF-1 signaling pathway, PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, and pathways in cancer. Further analysis identified the key components and core targets of ZZP against GERD, of which nobiletin, didymin, luteolin, and naringenin were key components, and PPARG, MMP9, JUN, TP53, PTGS2, EGFR, MAPK3, CASP3, AKT1, and VEGFA were the core targets. Molecular docking verified the stable bonds formed between the key components and the core targets.
Conclusions: The results of this study predict that the therapeutic effects of ZZP in GERD are mediated at least in part via PPARG, MMP9, JUN, TP53, PTGS2, EGFR, MAPK3, CASP3, AKT1, and VEGFA. These results may be useful in providing an experimental basis and new ideas for further research on ZZP in GERD.
Copyright © 2022 Jinke Huang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

