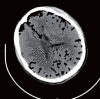
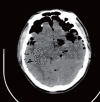
Traumatic tension pneumocephalus: A case report
- PMID: 35646210
- PMCID: PMC9108904
- DOI: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2022.053
Traumatic tension pneumocephalus: A case report
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- L'Hommedieu LM, Dingeldein MW, Tomei KL, Kilbane BJ. Acute management of tension pneumocephalus in a pediatric patient:a case report. J Emerg Med. 2018;54(1):112–5. - PubMed
-
- Luckett WH. Air in the ventricle of the brain following a fracture of the skull. J New Ment Dis. 1913;40:326–8.
-
- DelGaudio JM, Ingley AP. Treatment of pneumocephalus after endoscopic sinus and microscopic skull base surgery. Am J Otolaryngol. 2010;31(4):226–30. - PubMed
-
- Tripathy P, Mohapatra SSG, Ranjan SK, Sarangi GS, Mohanty S. Post-traumatic delayed intracerebral tension pneumatocele:a case report and review of literature. Indian J Neurotrauma. 2013;10(2):127–30.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources