PXR activation impairs hepatic glucose metabolism partly via inhibiting the HNF4 α-GLUT2 pathway
- PMID: 35646519
- PMCID: PMC9136535
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.09.031
PXR activation impairs hepatic glucose metabolism partly via inhibiting the HNF4 α-GLUT2 pathway
Abstract
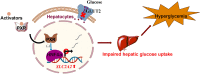
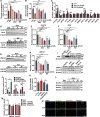
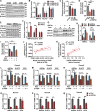
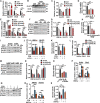
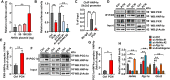
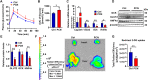
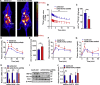
Drug-induced hyperglycemia/diabetes is a global issue. Some drugs induce hyperglycemia by activating the pregnane X receptor (PXR), but the mechanism is unclear. Here, we report that PXR activation induces hyperglycemia by impairing hepatic glucose metabolism due to inhibition of the hepatocyte nuclear factor 4-alpha (HNF4α)‒glucose transporter 2 (GLUT2) pathway. The PXR agonists atorvastatin and rifampicin significantly downregulated GLUT2 and HNF4α expression, and impaired glucose uptake and utilization in HepG2 cells. Overexpression of PXR downregulated GLUT2 and HNF4α expression, while silencing PXR upregulated HNF4α and GLUT2 expression. Silencing HNF4α decreased GLUT2 expression, while overexpressing HNF4α increased GLUT2 expression and glucose uptake. Silencing PXR or overexpressing HNF4α reversed the atorvastatin-induced decrease in GLUT2 expression and glucose uptake. In human primary hepatocytes, atorvastatin downregulated GLUT2 and HNF4α mRNA expression, which could be attenuated by silencing PXR. Silencing HNF4α downregulated GLUT2 mRNA expression. These findings were reproduced with mouse primary hepatocytes. Hnf4α plasmid increased Slc2a2 promoter activity. Hnf4α silencing or pregnenolone-16α-carbonitrile (PCN) suppressed the Slc2a2 promoter activity by decreasing HNF4α recruitment to the Slc2a2 promoter. Liver-specific Hnf4α deletion and PCN impaired glucose tolerance and hepatic glucose uptake, and decreased the expression of hepatic HNF4α and GLUT2. In conclusion, PXR activation impaired hepatic glucose metabolism partly by inhibiting the HNF4α‒GLUT2 pathway. These results highlight the molecular mechanisms by which PXR activators induce hyperglycemia/diabetes.
Keywords: Diabetes; Drug-induced hyperglycemia; Glucose transporter 2; Hepatic glucose uptake; Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4-alpha; Pregnane X receptor.
© 2022 Chinese Pharmaceutical Association and Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Liu M.Z., He H.Y., Luo J.Q., He F.Z., Chen Z.R., Liu Y.P., et al. Drug-induced hyperglycaemia and diabetes: pharmacogenomics perspectives. Arch Pharm Res. 2018;41:725–736. - PubMed
-
- Fathallah N., Slim R., Larif S., Hmouda H., Ben Salem C. Drug-induced hyperglycaemia and diabetes. Drug Saf. 2015;38:1153–1168. - PubMed
-
- Jain V., Patel R.K., Kapadia Z., Galiveeti S., Banerji M., Hope L. Drugs and hyperglycemia: a practical guide. Maturitas. 2017;104:80–83. - PubMed
-
- Luo G., Cunningham M., Kim S., Burn T., Lin J., Sinz M., et al. CYP3A4 induction by drugs: correlation between a pregnane X receptor reporter gene assay and CYP3A4 expression in human hepatocytes. Drug Metab Dispos. 2002;30:795–804. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

