Design of a highly potent GLP-1R and GCGR dual-agonist for recovering hepatic fibrosis
- PMID: 35646543
- PMCID: PMC9136578
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.12.016
Design of a highly potent GLP-1R and GCGR dual-agonist for recovering hepatic fibrosis
Abstract
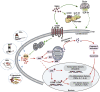
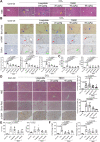
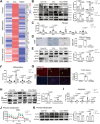
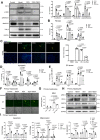
Currently, there is still no effective curative treatment for the development of late-stage liver fibrosis. Here, we have illustrated that TB001, a dual glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor/glucagon receptor (GLP-1R/GCGR) agonist with higher affinity towards GCGR, could retard the progression of liver fibrosis in various rodent models, with remarkable potency, selectivity, extended half-life and low toxicity. Four types of liver fibrosis animal models which were induced by CCl4, α-naphthyl-isothiocyanate (ANIT), bile duct ligation (BDL) and Schistosoma japonicum were used in our study. We found that TB001 treatment dose-dependently significantly attenuated liver injury and collagen accumulation in these animal models. In addition to decreased levels of extracellular matrix (ECM) accumulation during hepatic injury, activation of hepatic stellate cells was also inhibited via suppression of TGF-β expression as well as downstream Smad signaling pathways particularly in CCl4-and S. japonicum-induced liver fibrosis. Moreover, TB001 attenuated liver fibrosis through blocking downstream activation of pro-inflammatory nuclear factor kappa B/NF-kappa-B inhibitor alpha (NFκB/IKBα) pathways as well as c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK)-dependent induction of hepatocyte apoptosis. Furthermore, GLP-1R and/or GCGR knock-down results represented GCGR played an important role in ameliorating CCl4-induced hepatic fibrosis. Therefore, TB001 can be used as a promising therapeutic candidate for the treatment of multiple causes of hepatic fibrosis demonstrated by our extensive pre-clinical evaluation of TB001.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Candidate peptides; GCGR; GLP-1R; Inflammation; Liver fibrosis.
© 2022 Chinese Pharmaceutical Association and Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Design and discovery of a highly potent ultralong-acting GLP-1 and glucagon co-agonist for attenuating renal fibrosis.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024 Mar;14(3):1283-1301. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2023.11.020. Epub 2023 Nov 18. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024. PMID: 38486997 Free PMC article.
-
GLP-1 and glucagon receptor dual agonism ameliorates kidney allograft fibrosis by improving lipid metabolism.Front Immunol. 2025 Mar 31;16:1551136. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1551136. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40230860 Free PMC article.
-
Stapled, Long-Acting Xenopus GLP-1-Based Dual GLP-1/Glucagon Receptor Agonists with Potent Therapeutic Efficacy for Metabolic Disease.Mol Pharm. 2021 Aug 2;18(8):2906-2923. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.0c00995. Epub 2021 Jul 9. Mol Pharm. 2021. PMID: 34240881
-
Cooperation of liver cells in health and disease.Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2001;161:III-XIII, 1-151. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-56553-3. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11729749 Review.
-
Mechanism-guided drug development and treatment for liver fibrosis: a clinical perspective.Front Pharmacol. 2025 May 26;16:1574385. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1574385. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40492139 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Design and discovery of a highly potent ultralong-acting GLP-1 and glucagon co-agonist for attenuating renal fibrosis.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024 Mar;14(3):1283-1301. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2023.11.020. Epub 2023 Nov 18. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024. PMID: 38486997 Free PMC article.
-
Glucagon-Like Peptide-1: New Regulator in Lipid Metabolism.Diabetes Metab J. 2024 May;48(3):354-372. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2023.0277. Epub 2024 Apr 1. Diabetes Metab J. 2024. PMID: 38650100 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Macrophage Signaling Pathways in Health and Disease: From Bench to Bedside Applications.MedComm (2020). 2025 Jun 16;6(7):e70256. doi: 10.1002/mco2.70256. eCollection 2025 Jul. MedComm (2020). 2025. PMID: 40529613 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Novel Tetra-Specific Drug C-192, Conjugated Using UniStac, Alleviates Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis in an MCD Diet-Induced Mouse Model.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Nov 13;16(11):1601. doi: 10.3390/ph16111601. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38004466 Free PMC article.
-
The Novel Long-Acting Peptide S6-FA Attenuates Liver Fibrosis In Vitro and In Vivo.ACS Omega. 2025 Feb 27;10(9):9661-9674. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c10956. eCollection 2025 Mar 11. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 40092780 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hernandez-Gea V., Friedman S.L. Pathogenesis of liver fibrosis. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2011;6:425–456. - PubMed
-
- Tsuchida T., Friedman S.L. Mechanisms of hepatic stellate cell activation. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;14:397–411. - PubMed
-
- Mannaerts I., Leite S.B., Verhulst S., Claerhout S., Eysackers N., Thoen L.F., et al. The Hippo pathway effector YAP controls mouse hepatic stellate cell activation. J Hepatol. 2015;63:679–688. - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

