Effect of Angiogenesis and Lymphangiogenesis in Diesel Exhaust Particles Inhalation in Mouse Model of LPS Induced Acute Otitis Media
- PMID: 35646744
- PMCID: PMC9132252
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.824575
Effect of Angiogenesis and Lymphangiogenesis in Diesel Exhaust Particles Inhalation in Mouse Model of LPS Induced Acute Otitis Media
Abstract
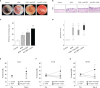
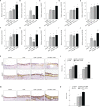
Lymphangiogenesis and angiogenesis might have significant involvement in the pathogenesis of otitis media with effusion. This study investigated the effect of diesel exhaust particles (DEP) on inflammation and lymphangiogenesis in a mouse model of acute otitis media (AOM). BALB/c mice were injected with LPS and exposed to 100 µg/m3 DEP. The mice were divided into four groups: control (no stimulation), AOM, AOM + DEP, and DEP + AOM. The effects of DEP inhalation pre- and post-DEP induction were estimated based on measurements of the auditory brainstem response, mRNA levels of lymphangiogenesis-related genes and cytokines, and histology of the middle ear. Cell viability of human middle ear epithelial cells decreased in a dose-response manner at 24 and 48 hours post-DEP exposure. DEP alone did not induce AOM. AOM-induced mice with pre- or post-DEP exposure showed thickened middle ear mucosa and increased expression of TNF-α and IL1-β mRNA levels compared to the control group, but increased serum IL-1β levels were not found in the AOM + Post DEP. The mRNA expression of TLR4, VEGFA, VEGFAC, and VEGFR3 was increased by pre-AOM DEP exposure. The expression of VEFGA protein was stronger in the AOM + Post DEP group than in any other group. The expression of CD31 and CD45 markers in the mouse middle ear tissue was higher in the Pre DEP + AOM group than in the AOM group. This result implies that pre-exposure to DEP more strongly increases inflammation and lymphangiogenesis in a mouse model of acute otitis media.
Keywords: angiogenesis; diesel exhaust particles; lipopolysaccharides; lymphangiogenesis; otitis media.
Copyright © 2022 Kim, Choi, Kim, Jang, Suh, Lee, Oh and Park.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Chun Y. M., Moon S. K., Lee H. Y., Webster P., Brackmann D. E., Rhim J. S., et al. (2002). Immortalization of Normal Adult Human Middle Ear Epithelial Cells Using a Retrovirus Containing the E6/E7 Genes of Human Papillomavirus Type 16. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol 111, 507–517. doi: 10.1177/000348940211100606 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

