Co-Delivery of Doxycycline and Hydroxychloroquine Using CdTe-Labeled Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for Treatment of Acute and Chronic Brucellosis
- PMID: 35646816
- PMCID: PMC9130827
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2022.890252
Co-Delivery of Doxycycline and Hydroxychloroquine Using CdTe-Labeled Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for Treatment of Acute and Chronic Brucellosis
Abstract
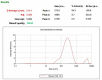
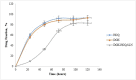
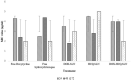
Brucellosis is a systemic disease in both acute and chronic forms which can affect any organ or tissue in the body. One of the biggest issues in treating this disease is its relapse. In this study, a complete treatment of brucellosis was evaluated using enhanced performance of doxycycline and hydroxychloroquine drugs by using solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) conjugated cadmium-telluride quantum dots. The double emulsion method was used to prepare SLN and cadmium-telluride quantum dots. The physicochemical properties of NPs were determined. The effect of nanoparticle-loaded antibiotics against Brucella melitensis was determined by well diffusion, minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC), cell culture, and animal studies. The means of particle size, PDI, zeta potential, drugs loading, and encapsulation efficiency were 214 ± 25 nm, 0.385 ± 0.022, -18.7 ± 2.3 mV, 17.7 ± 1.5%, and 94.15 ± 2.6%, respectively. The results of FTIR and DSC showed that no chemical reaction occurred between the components of the NPs. The effect of free drug and NPs on bacteria was the same by well diffusion and MIC method. Drug-loaded NPs significantly reduced the number of CFUs in the cell line and acute and chronic brucellosis compared to the free drug. In conclusion, the synthesized nanoparticles were safe and green. With the slow release of the drug (100 h), the accumulation of the drug at the bacterial site increases and causes a greater effect on the B. melitensis and improves the disease of brucellosis. The use of synthesized nanodrugs in this study had promising therapeutic results.
Keywords: Brucella melitensis; brucellosis; doxycycline; hydroxychloroquine; solid lipid nanoparticles.
Copyright © 2022 Hosseini, Farmany, Alikhani, Taheri, Asl, Alamian and Arabestani.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Abd Elbaser E., Mohammed H. (2018). Brucellosis Relapse: a Retrospective Study of Risk Factors Among Saudi Patients. Afro-Egyptian J. Infect. Endemic Dis. 8, 149–154. 10.21608/aeji.2018.13526 - DOI
-
- Arshad R., Pal K., Sabir F., Rahdar A., Bilal M., Shahnaz G., et al. (2021a). A Review of the Nanomaterials Use for the Diagnosis and Therapy of salmonella Typhi. J. Mol. Struct. 1230, 129928. 10.1016/j.molstruc.2021.129928 - DOI
-
- Arshad R., Tabish T. A., Kiani M. H., Ibrahim I. M., Shahnaz G., Rahdar A., et al. (2021b). A Hyaluronic Acid Functionalized Self-Nano-Emulsifying Drug Delivery System (SNEDDS) for Enhancement in Ciprofloxacin Targeted Delivery against Intracellular Infection. Nanomaterials 11, 1086. 10.3390/nano11051086 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bardajee G. R., Bayat M., Nasri S., Vancaeyzeele C. (2018). pH-Responsive Fluorescent Dye-Labeled Metal-Chelating Polymer with Embedded Cadmium telluride Quantum Dots for Controlled Drug Release of Doxorubicin. Reactive Funct. Polym. 133, 45–56. 10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2018.09.008 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

