Neuroimmune Interaction: A Widespread Mutual Regulation and the Weapons for Barrier Organs
- PMID: 35646918
- PMCID: PMC9130600
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2022.906755
Neuroimmune Interaction: A Widespread Mutual Regulation and the Weapons for Barrier Organs
Abstract
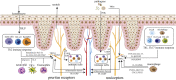
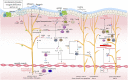
Since the embryo, the nervous system and immune system have been interacting to regulate each other's development and working together to resist harmful stimuli. However, oversensitive neural response and uncontrolled immune attack are major causes of various diseases, especially in barrier organs, while neural-immune interaction makes it worse. As the first defense line, the barrier organs give a guarantee to maintain homeostasis in external environment. And the dense nerve innervation and abundant immune cell population in barrier organs facilitate the neuroimmune interaction, which is the physiological basis of multiple neuroimmune-related diseases. Neuroimmune-related diseases often have complex mechanisms and require a combination of drugs, posing challenges in finding etiology and treatment. Therefore, it is of great significance to illustrate the specific mechanism and exact way of neuro-immune interaction. In this review, we first described the mutual regulation of the two principal systems and then focused on neuro-immune interaction in the barrier organs, including intestinal tract, lungs and skin, to clarify the mechanisms and provide ideas for clinical etiology exploration and treatment.
Keywords: barrier organ; immune; nerve; neuroimmune crosstalk; neuropeptide; neurotransmitter.
Copyright © 2022 Zhu, Duan, Wang, Deng and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

