Preliminary Investigation of the Biomarkers of Acute Renal Transplant Rejection Using Integrated Proteomics Studies, Gene Expression Omnibus Datasets, and RNA Sequencing
- PMID: 35646951
- PMCID: PMC9133438
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.905464
Preliminary Investigation of the Biomarkers of Acute Renal Transplant Rejection Using Integrated Proteomics Studies, Gene Expression Omnibus Datasets, and RNA Sequencing
Abstract
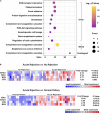
A kidney transplant is often the best treatment for end-stage renal disease. Although immunosuppressive therapy sharply reduces the occurrence of acute allograft rejection (AR), it remains the main cause of allograft dysfunction. We aimed to identify effective biomarkers for AR instead of invasive kidney transplant biopsy. We integrated the results of several proteomics studies related to AR and utilized public data sources. Gene ontology (GO) and pathway analyses were used to identify important biological processes and pathways. The performance of the identified proteins was validated using several public gene expression omnibus (GEO) datasets. Samples that performed well were selected for further validation through RNA sequencing of peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with AR (n = 16) and non-rejection (n = 19) from our medical center. A total of 25 differentially expressed proteins (DEPs) overlapped in proteomic studies of urine and blood samples. GO analysis showed that the DEPs were mainly involved in the immune system and blood coagulation. Pathway analysis showed that the complement and coagulation cascade pathways were well enriched. We found that immunoglobulin heavy constant alpha 1 (IGHA1) and immunoglobulin κ constant (IGKC) showed good performance in distinguishing AR from non-rejection groups validated with several GEO datasets. Through RNA sequencing, the combination of IGHA1, IGKC, glomerular filtration rate, and donor age showed good performance in the diagnosis of AR with ROC AUC 91.4% (95% CI: 82-100%). Our findings may contribute to the discovery of potential biomarkers for AR monitoring.
Keywords: RNA sequencing; biomarkers; gene expression omnibus datasets; proteomics studies; renal allograft rejection.
Copyright © 2022 Han, Zhao, Wang, Wang, Song, Haller, Jiang and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Pre-transplant Transcriptional Signature in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells of Acute Renal Allograft Rejection.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Jan 7;8:799051. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.799051. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35071278 Free PMC article.
-
SLAMF8 Participates in Acute Renal Transplant Rejection via TLR4 Pathway on Pro-Inflammatory Macrophages.Front Immunol. 2022 Apr 1;13:846695. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.846695. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35432371 Free PMC article.
-
Differentially expressed RNA from public microarray data identifies serum protein biomarkers for cross-organ transplant rejection and other conditions.PLoS Comput Biol. 2010 Sep 23;6(9):e1000940. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000940. PLoS Comput Biol. 2010. PMID: 20885780 Free PMC article.
-
Non-invasive approaches in the diagnosis of acute rejection in kidney transplant recipients, part II: omics analyses of urine and blood samples.Clin Kidney J. 2017 Feb;10(1):106-115. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfw077. Epub 2016 Sep 6. Clin Kidney J. 2017. PMID: 28643819 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-invasive cardiac allograft rejection surveillance: reliability and clinical value for prevention of heart failure.Heart Fail Rev. 2021 Mar;26(2):319-336. doi: 10.1007/s10741-020-10023-3. Epub 2020 Sep 5. Heart Fail Rev. 2021. PMID: 32889634 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of Renal Transplantation Rejection Biomarkers in Blood Using the Systems Biology Approach.Iran Biomed J. 2023 Aug 23;27(6):375-87. doi: 10.52547/ibj.3871. Online ahead of print. Iran Biomed J. 2023. PMID: 38224029 Free PMC article.
-
Urinary CXCL-10, a prognostic biomarker for kidney graft injuries: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Nephrol. 2024 Sep 4;25(1):292. doi: 10.1186/s12882-024-03728-2. BMC Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 39232662 Free PMC article.
-
Uncover diagnostic immunity/hypoxia/ferroptosis/epithelial mesenchymal transformation-related CCR5, CD86, CD8A, ITGAM, and PTPRC in kidney transplantation patients with allograft rejection.Ren Fail. 2022 Dec;44(1):1850-1865. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2022.2141648. Ren Fail. 2022. PMID: 36330810 Free PMC article.
-
Single-Cell Sequence and Machine Learning Identify a CD79A+B Cells-Related Transcriptional Signature for Predicting Clinical Outcomes and Immune Microenvironment in Breast Cancer.Cancer Inform. 2025 Jul 26;24:11769351251360675. doi: 10.1177/11769351251360675. eCollection 2025. Cancer Inform. 2025. PMID: 40734705 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple omics-based machine learning reveals peripheral blood immune cell landscape during acute rejection of kidney transplantation and constructs a precise non-invasive diagnostic strategy.Mamm Genome. 2025 Jul 7. doi: 10.1007/s00335-025-10149-5. Online ahead of print. Mamm Genome. 2025. PMID: 40624201
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

