Transcriptomic Analysis Revealed an Important Role of Peroxisome-Proliferator-Activated Receptor Alpha Signaling in Src Homology Region 2 Domain-Containing Phosphatase-1 Insufficiency Leading to the Development of Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury
- PMID: 35646989
- PMCID: PMC9134314
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.847512
Transcriptomic Analysis Revealed an Important Role of Peroxisome-Proliferator-Activated Receptor Alpha Signaling in Src Homology Region 2 Domain-Containing Phosphatase-1 Insufficiency Leading to the Development of Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury
Abstract
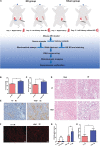
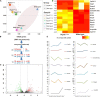
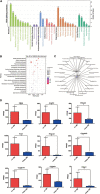
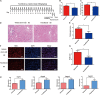
In kidney transplantation, the donor kidney inevitably undergoes ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI). It is of great importance to study the pathogenesis of IRI and find effective measures to attenuate acute injury of renal tubules after ischemia-reperfusion. Our previous study found that Src homology region 2 domain-containing phosphatase-1 (SHP-1) insufficiency aggravates renal IRI. In this study, we systematically analyzed differences in the expression profiles of SHP-1 (encoded by Ptpn6)-insufficient mice and wild-type mice by RNA-seq. We found that a total of 161 genes showed at least a twofold change, with a false discovery rate <0.05 in Ptpn6 +/mev mice after IRI and 42 genes showing more than a fourfold change. Of the eight genes encoding proteins with immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motifs (ITIMs) that bind to Ptpn6, three were upregulated, and five were downregulated. We found that for the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) with a fold change >2, the most significantly enriched Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathways were the cell division pathway and peroxisome-proliferator activated receptor PPARα signaling pathways. Furthermore, the downregulated genes of the PPARα signaling pathway were mainly related to fatty acid absorption and degradation. Using an agonist of the PPARα signaling pathway, fenofibrate, we found that renal IRI was significantly attenuated in Ptpn6 +/mev mice. In summary, our results show that insufficiency of SHP-1 inhibits the expression of genes in the PPARα signaling pathway, thereby leading to increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) and exacerbating the renal IRI. The PPARα signaling agonist fenofibrate partially attenuates renal IRI induced by SHP-1 insufficiency.
Keywords: PPARα signaling; SHP-1; bioinformatics; kidney transplantation; renal ischemia-reperfusion injury.
Copyright © 2022 Yan, Sui, Tian, Fu, Li, Chen, Zeng and Ding.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Blanchette J, Racette N, Faure R, Siminovitch KA, Olivier M. Leishmania-induced increases in activation of macrophage SHP-1 tyrosine phosphatase are associated with impaired IFN-γ-triggered JAK2 activation. Eur J Immunol. (1999) 29:3737–44. 10.1002/(SICI)1521-4141(199911)29:113.0.CO;2-S - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

