Synergistic inhibition of hepatitis C virus infection by a novel microtubule inhibitor in combination with daclatasvir
- PMID: 35647321
- PMCID: PMC9136107
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2022.101283
Synergistic inhibition of hepatitis C virus infection by a novel microtubule inhibitor in combination with daclatasvir
Abstract
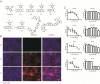
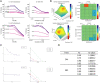
Even though substantial progress has been made in the treatment of hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection, viral resistance and relapse still occur in some patients and additional therapeutic approaches may ultimately be needed should viral resistance become more prevalent. Microtubules play important roles in several HCV life cycle events, including cell attachment, entry, cellular transportation, morphogenesis and progeny secretion steps. Therefore, it was hypothesized that microtubular inhibition might be a novel approach for the treatment of HCV infection. Here, the inhibitory effects of our recently developed microtubule inhibitors were studied in the HCV replicon luciferase reporter system and the infectious system. In addition, the combination responses of microtubule inhibitors with daclatasvir, which is a clinically used HCV NS5A inhibitor, were also evaluated. Our results indicated that microtubule targeting had activity against HCV replication and showed synergistic effect with a current clinical drug.
Keywords: Combinational therapy; Hepatitis C virus; Microtubule inhibitor; Viral resistance.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Choo Q.-L., Kuo G., Weiner A.J., Overby L.R., Bradley D.W., Houghton M. Isolation of a cDNA clone derived from a blood-borne non-A, non-B viral hepatitis genome. Science. 1989;244:359–362. - PubMed
-
- Lahser F.C., Bystol K., Curry S., McMonagle P., Xia E., Ingravallo P., Chase R., Liu R., Black T., Hazuda D., Howe A.Y., Asante-Appiah E. The combination of Grazoprevir, a hepatitis C virus (HCV) NS3/4A protease inhibitor, and Elbasvir, an HCV NS5A inhibitor, demonstrates a high genetic barrier to resistance in HCV genotype 1a replicons. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016;60:2954–2964. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00051-16. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

