The effect of prior knowledge of color on reaction time depends on visual modality
- PMID: 35647346
- PMCID: PMC9133575
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e09469
The effect of prior knowledge of color on reaction time depends on visual modality
Abstract
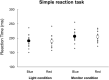
Prior knowledge of color, such as traffic rules (blue/green and red mean "go" and "stop" respectively), can influence reaction times (RTs). Specifically, in a Go/No-go task, where signals were presented by a light-emitting diode (LED) lighting device, RT has been reported to be longer when responding to a red signal and withholding the response to a blue signal (Red Go/Blue No-go task) than when responding to a blue signal and withholding the response to a red signal (Blue Go/Red No-go task). In recent years, a driving simulator has been shown to be effective in evaluation and training of driving skills of dementia and stroke patients. However, it is unknown whether the change in RT observed with the LED lighting device can be replicated with a monitor presenting signals that are different from the real traffic lights in terms of depth and texture. The purpose of this study was to elucidate whether a difference in visual modality (LED and monitor) influences the effect of prior knowledge of color on RTs. Fifteen participants performed a simple reaction task (Blue and Red signals), a Blue Go/Red No-go task, and a Red Go/Blue No-go task. Signals were presented from an LED lighting device (Light condition) and a liquid crystal display (LCD) monitor (Monitor condition). The results showed that there was no significant difference in simple RT by signal color in both conditions. In the Go/No-go task, there was a significant interaction between the type of signal presentation device and the color of signal. Although the RT was significantly longer in the Red Go/Blue No-go than Blue Go/Red No-go task in the Light condition, there was no significant difference in RT between the Blue Go/Red No-go and Red Go/Blue No-go tasks in the Monitor condition. It is interpreted that blue and red signals presented from the LCD monitor were insufficient to evoke a perception of traffic lights as compared to the LED. This study suggests that a difference in the presentation modality (LED and monitor) of visual information can influence the level of object perception and consequently the effect of prior knowledge on behavioral responses.
Keywords: Go/No-go task; Prior knowledge of color; Reaction time; Visual modality.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Color-induced cognitive conflicts affect muscle activity prior to gait initiation in the Go/No-go task.Front Hum Neurosci. 2024 Oct 2;18:1463220. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2024.1463220. eCollection 2024. Front Hum Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39416685 Free PMC article.
-
Reaction time and brain oscillations in Go/No-go tasks with different meanings of stimulus color.Cortex. 2023 Dec;169:203-219. doi: 10.1016/j.cortex.2023.07.011. Epub 2023 Oct 19. Cortex. 2023. PMID: 37948875
-
The Effect of Prior Knowledge of Color on Behavioral Responses and Event-Related Potentials During Go/No-go Task.Front Hum Neurosci. 2021 Jun 10;15:674964. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2021.674964. eCollection 2021. Front Hum Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34177494 Free PMC article.
-
The simple perfection of quantum correlation in human vision.Prog Neurobiol. 2006 Jan;78(1):38-60. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2005.11.006. Epub 2005 Dec 27. Prog Neurobiol. 2006. PMID: 16377059 Review.
-
Go Red for Women at 20 Years: Where Do We Go From Here?Circulation. 2025 Feb 18;151(7):e39-e40. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.124.073637. Epub 2025 Feb 17. Circulation. 2025. PMID: 39960980 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Color-induced cognitive conflicts affect muscle activity prior to gait initiation in the Go/No-go task.Front Hum Neurosci. 2024 Oct 2;18:1463220. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2024.1463220. eCollection 2024. Front Hum Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39416685 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Iacoboni M. Visuo-motor integration and control in the human posterior parietal cortex: evidence from TMS and fMRI. Neuropsychologia. 2006;44:2691–2699. - PubMed
-
- Caylak E. The studies about phonological deficit theory in children with developmental dyslexia: review. Am. J. Neurosci. 2010;1:1–12.
-
- Yotani K., Tamaki H., Yuki A., Kirimoto H., Kitada K., Ogita F., Takekura H. Response training shortens visuo-motor related time in athletes. Int. J. Sports Med. 2011;32:586–590. - PubMed
-
- Kida N., Oda S., Matsumura M. Intensive baseball practice improves the Go/Nogo reaction time, but not the simple reaction time. Cognit. Brain Res. 2005;22:257–264. - PubMed
-
- Jodo E., Kayama Y. Relation of a negative ERP component to response inhibition in a Go/No-go task. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1992;82:477–482. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

