Application of exosomes for the alleviation of COVID-19-related pathologies
- PMID: 35647674
- PMCID: PMC9348296
- DOI: 10.1002/cbf.3720
Application of exosomes for the alleviation of COVID-19-related pathologies
Abstract
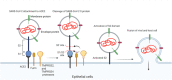
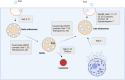
The pandemic of COVID-19 caused worldwide concern. Due to the lack of appropriate medications and the inefficiency of commercially available vaccines, lots of efforts are being made to develop de novo therapeutic modalities. Besides this, the possibility of several genetic mutations in the viral genome has led to the generation of resistant strains such as Omicron against neutralizing antibodies and vaccines, leading to worsening public health status. Exosomes (Exo), nanosized vesicles, possess several therapeutic properties that participate in intercellular communication. The discovery and application of Exo in regenerative medicine have paved the way for the alleviation of several pathologies. These nanosized particles act as natural bioshuttles and transfer several biomolecules and anti-inflammatory cytokines. To date, several approaches are available for the administration of Exo into the targeted site inside the body, although the establishment of standard administration routes remains unclear. As severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 primarily affects the respiratory system, we here tried to highlight the transplantation of Exo in the alleviation of COVID-19 pathologies.
Keywords: COVID-19; exosomes; paracrine interaction; regenerative potential; stem cell; therapeutic effects.
© 2022 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Rezabakhsh A, Ala A, Khodaei SH. Novel coronavirus (COVID‐19): a new emerging pandemic threat. J Res Clin Med. 2020;8:5.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

