Temporal assessment of lesion morphology on radiological images beyond lesion volumes-a proof-of-principle study
- PMID: 35648210
- PMCID: PMC9712148
- DOI: 10.1007/s00330-022-08894-1
Temporal assessment of lesion morphology on radiological images beyond lesion volumes-a proof-of-principle study
Abstract
Objectives: To develop a general framework to assess temporal changes in lesion morphology on radiological images beyond volumetric changes and to test whether cocaine abstinence changes coronary plaque structure on serial coronary CT angiography (CTA).
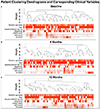
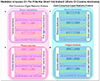
Methods: Chronic cocaine users with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection were prospectively enrolled to undergo cash-based contingency management to achieve cocaine abstinence. Participants underwent coronary CTA at baseline and 6 and 12 months following recruitment. We segmented all coronary plaques and extracted 1103 radiomic features. We implemented weighted correlation network analysis to derive consensus eigen radiomic features (named as different colors) and used linear mixed models and mediation analysis to assess whether cocaine abstinence affects plaque morphology correcting for clinical variables and plaque volumes and whether serum biomarkers causally mediate these changes. Furthermore, we used Bayesian hidden Markov network changepoint analysis to assess the potential rewiring of the radiomic network.
Results: Sixty-nine PLWH (median age 55 IQR: 52-59 years, 19% female) completed the study, of whom 26 achieved total abstinence. Twenty consensus eigen radiomic features were derived. Cocaine abstinence significantly affected the pink and cyan eigen features (-0.04 CI: [-0.06; -0.02], p = 0.0009; 0.03 CI: [0.001; 0.04], p = 0.0017, respectively). These effects were mediated through changes in endothelin-1 levels. In abstinent individuals, we observed significant rewiring of the latent radiomic signature network.
Conclusions: Using our proposed framework, we found 1 year of cocaine abstinence to significantly change specific latent coronary plaque morphological features and rewire the latent morphologic network above and beyond changes in plaque volumes and clinical characteristics.
Key points: • We propose a general methodology to decompose the latent morphology of lesions on radiological images using a radiomics-based systems biology approach. • As a proof-of-principle, we show that 1 year of cocaine abstinence results in significant changes in specific latent coronary plaque morphologic features and rewiring of the latent morphologic network above and beyond changes in plaque volumes and clinical characteristics. • We found endothelin-1 levels to mediate these structural changes providing potential pathological pathways warranting further investigation.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Cocaine addiction; Coronary artery disease; Longitudinal studies; Precision medicine.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to European Society of Radiology.
Figures



References
-
- AstraZeneca, Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction Study G (2023) Efficacy and Safety of MEDI6570 in Patients With a History of Myocardial Infarction,
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

