The Jena Voice Learning and Memory Test (JVLMT): A standardized tool for assessing the ability to learn and recognize voices
- PMID: 35648317
- PMCID: PMC10126074
- DOI: 10.3758/s13428-022-01818-3
The Jena Voice Learning and Memory Test (JVLMT): A standardized tool for assessing the ability to learn and recognize voices
Abstract
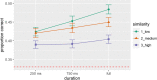
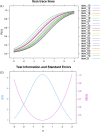
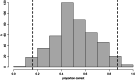
The ability to recognize someone's voice spans a broad spectrum with phonagnosia on the low end and super-recognition at the high end. Yet there is no standardized test to measure an individual's ability of learning and recognizing newly learned voices with samples of speech-like phonetic variability. We have developed the Jena Voice Learning and Memory Test (JVLMT), a 22-min test based on item response theory and applicable across languages. The JVLMT consists of three phases in which participants (1) become familiarized with eight speakers, (2) revise the learned voices, and (3) perform a 3AFC recognition task, using pseudo-sentences devoid of semantic content. Acoustic (dis)similarity analyses were used to create items with various levels of difficulty. Test scores are based on 22 items which had been selected and validated based on two online studies with 232 and 454 participants, respectively. Mean accuracy in the JVLMT is 0.51 (SD = .18) with an empirical (marginal) reliability of 0.66. Correlational analyses showed high and moderate convergent validity with the Bangor Voice Matching Test (BVMT) and Glasgow Voice Memory Test (GVMT), respectively, and high discriminant validity with a digit span test. Four participants with potential super recognition abilities and seven participants with potential phonagnosia were identified who performed at least 2 SDs above or below the mean, respectively. The JVLMT is a promising research and diagnostic screening tool to detect both impairments in voice recognition and super-recognition abilities.
Keywords: IRT; Individual differences; Phonagnosia; Voice recognition.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

