Structural basis for interaction between CLAMP and MSL2 proteins involved in the specific recruitment of the dosage compensation complex in Drosophila
- PMID: 35648444
- PMCID: PMC9226498
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkac455
Structural basis for interaction between CLAMP and MSL2 proteins involved in the specific recruitment of the dosage compensation complex in Drosophila
Abstract
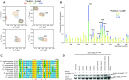
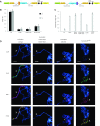
Transcriptional regulators select their targets from a large pool of similar genomic sites. The binding of the Drosophila dosage compensation complex (DCC) exclusively to the male X chromosome provides insight into binding site selectivity rules. Previous studies showed that the male-specific organizer of the complex, MSL2, and ubiquitous DNA-binding protein CLAMP directly interact and play an important role in the specificity of X chromosome binding. Here, we studied the highly specific interaction between the intrinsically disordered region of MSL2 and the N-terminal zinc-finger C2H2-type (C2H2) domain of CLAMP. We obtained the NMR structure of the CLAMP N-terminal C2H2 zinc finger, which has a classic C2H2 zinc-finger fold with a rather unusual distribution of residues typically used in DNA recognition. Substitutions of residues in this C2H2 domain had the same effect on the viability of males and females, suggesting that it plays a general role in CLAMP activity. The N-terminal C2H2 domain of CLAMP is highly conserved in insects. However, the MSL2 region involved in the interaction is conserved only within the Drosophila genus, suggesting that this interaction emerged during the evolution of a mechanism for the specific recruitment of the DCC on the male X chromosome in Drosophilidae.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Interaction of MLE with CLAMP zinc finger is involved in proper MSL proteins binding to chromosomes in Drosophila.Open Biol. 2024 Mar;14(3):230270. doi: 10.1098/rsob.230270. Epub 2024 Mar 13. Open Biol. 2024. PMID: 38471568 Free PMC article.
-
The simultaneous interaction of MSL2 with CLAMP and DNA provides redundancy in the initiation of dosage compensation in Drosophila males.Development. 2019 Aug 23;146(19):dev179663. doi: 10.1242/dev.179663. Development. 2019. PMID: 31320325
-
The DNA binding CXC domain of MSL2 is required for faithful targeting the Dosage Compensation Complex to the X chromosome.Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Jun;38(10):3209-21. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq026. Epub 2010 Feb 5. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010. PMID: 20139418 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin mechanisms in Drosophila dosage compensation.Prog Mol Subcell Biol. 2005;38:123-49. doi: 10.1007/3-540-27310-7_5. Prog Mol Subcell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15881893 Review.
-
Dosage compensation and chromatin structure in Drosophila.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1996 Aug;6(4):496-501. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(96)80073-6. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1996. PMID: 8791531 Review.
Cited by
-
Physical interaction between MSL2 and CLAMP assures direct cooperativity and prevents competition at composite binding sites.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Sep 22;51(17):9039-9054. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad680. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 37602401 Free PMC article.
-
Dimerization Activity of a Disordered N-Terminal Domain from Drosophila CLAMP Protein.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 31;23(7):3862. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073862. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35409222 Free PMC article.
-
Novel protein-truncating variants of a chromatin-modifying gene MSL2 in syndromic neurodevelopmental disorders.Eur J Hum Genet. 2024 Jul;32(7):879-883. doi: 10.1038/s41431-024-01576-0. Epub 2024 May 3. Eur J Hum Genet. 2024. PMID: 38702431 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of MLE with CLAMP zinc finger is involved in proper MSL proteins binding to chromosomes in Drosophila.Open Biol. 2024 Mar;14(3):230270. doi: 10.1098/rsob.230270. Epub 2024 Mar 13. Open Biol. 2024. PMID: 38471568 Free PMC article.
-
Dosage Compensation in Drosophila: Its Canonical and Non-Canonical Mechanisms.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 19;23(18):10976. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810976. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142884 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Samata M., Akhtar A.. Dosage compensation of the X chromosome: a complex epigenetic assignment involving chromatin regulators and long noncoding RNAs. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2018; 87:323–350. - PubMed
-
- Lucchesi J.C. Transcriptional modulation of entire chromosomes: dosage compensation. J. Genet. 2018; 97:357–364. - PubMed
-
- Beckmann K., Grskovic M., Gebauer F., Hentze M.W.. A dual inhibitory mechanism restricts msl-2 mRNA translation for dosage compensation in Drosophila. Cell. 2005; 122:529–540. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

