Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 and influenza A virus co-infection alters viral tropism and haematological composition in Syrian hamsters
- PMID: 35648595
- PMCID: PMC9347909
- DOI: 10.1111/tbed.14601
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 and influenza A virus co-infection alters viral tropism and haematological composition in Syrian hamsters
Abstract
The ongoing coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic and its overlap with the influenza season lead to concerns over severe disease caused by the influenza virus and severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) co-infections. Using a Syrian hamster co-infection model with SARS-CoV-2 and the pandemic influenza virus A/California/04/2009 (H1N1), we found (a) more severe disease in co-infected animals, compared to those infected with influenza virus alone but not SARS-CoV-2 infection alone; (b) altered haematological changes in only co-infected animals and (c) altered influenza virus tropism in the respiratory tracts of co-infected animals. Overall, our study revealed that co-infection with SARS-CoV-2 and influenza virus is associated with altered disease severity and tissue tropism, as well as haematological changes, compared to infection with either virus alone.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; co-infection; haematological change; influenza A virus; viral tropism.
© 2022 The Authors. Transboundary and Emerging Diseases published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
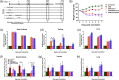
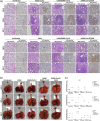
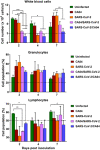
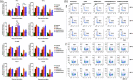
References
-
- Dovas, C. I. , Papanastassopoulou, M. , Georgiadis, M. P. , Chatzinasiou, E. , Maliogka, V. I. , & Georgiades, G. K. (2010). Detection and quantification of infectious avian influenza A (H5N1) virus in environmental water by using real‐time reverse transcription‐PCR. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 76, 2165–2174. 10.1128/AEM.01929-09 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Espitia, C. M. , Zhao, W. , Saldarriaga, O. , Osorio, Y. , Harrison, L. M. , Cappello, M. , Travi, B. L. , & Melby, P. C. (2010). Duplex real‐time reverse transcriptase PCR to determine cytokine mRNA expression in a hamster model of New World cutaneous leishmaniasis. BMC Immunology, 11, 31. 10.1186/1471-2172-11-31 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Huang, C. , Wang, Y. , Li, X. , Ren, L. , Zhao, J. , Hu, Y. , Zhang, L. , Fan, G. , Xu, J. , Gu, X. , Cheng, Z. , Yu, T. , Xia, J. , Wei, Y. , Wu, W. , Xie, X. , Yin, W. , Li, H. , Liu, M. , … Cao, B. (2020). Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet, 395, 497–506. 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 2020R1A2C2009262/National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Korean government
- 2021M3A91208049511/Bio & Medical Technology Development Program of the National Research Foundation (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science & ICT
- 2021M3H9A3020933/Bio & Medical Technology Development Program of the National Research Foundation (NRF) and funded by the Korean government (MSIT)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

