Spatial interplay patterns of cancer nuclei and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) predict clinical benefit for immune checkpoint inhibitors
- PMID: 35648850
- PMCID: PMC9159577
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abn3966
Spatial interplay patterns of cancer nuclei and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) predict clinical benefit for immune checkpoint inhibitors
Abstract
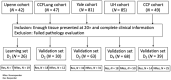
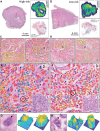
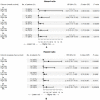
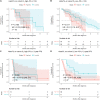
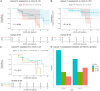
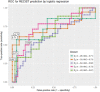
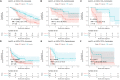
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) show prominent clinical activity across multiple advanced tumors. However, less than half of patients respond even after molecule-based selection. Thus, improved biomarkers are required. In this study, we use an image analysis to capture morphologic attributes relating to the spatial interaction and architecture of tumor cells and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) from digitized H&E images. We evaluate the association of image features with progression-free (PFS) and overall survival in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) (N = 187) and gynecological cancer (N = 39) patients treated with ICIs. We demonstrated that the classifier trained with NSCLC alone was associated with PFS in independent NSCLC cohorts and also in gynecological cancer. The classifier was also associated with clinical outcome independent of clinical factors. Moreover, the classifier was associated with PFS even with low PD-L1 expression. These findings suggest that image analysis can be used to predict clinical end points in patients receiving ICI.
Figures

References
-
- Luke J. J., Flaherty K. T., Ribas A., Long G. V., Targeted agents and immunotherapies: Optimizing outcomes in melanoma. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 14, 463–482 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Antonia S. J., Vansteenkiste J. F., Moon E., Immunotherapy: Beyond anti-PD-1 and anti-PD-L1 therapies. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 35, e450-458 (2016). - PubMed
Grants and funding
- UL1 TR002548/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA216579/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001863/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- C06 RR012463/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA199374/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R43 EB028736/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA239055/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA249992/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA220581/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA202752/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA208236/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA248226/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX004121/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- R01 CA257612/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA254566/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

