BRAF-Mutated Advanced Colorectal Cancer: A Rapidly Changing Therapeutic Landscape
- PMID: 35649231
- PMCID: PMC9390817
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.21.02541
BRAF-Mutated Advanced Colorectal Cancer: A Rapidly Changing Therapeutic Landscape
Abstract
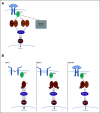
BRAF-mutated advanced colorectal cancer is a relatively small but critical subset of this tumor type on the basis of prognostic and predictive implications. BRAF alterations in colorectal cancer are classified into three functional categories on the basis of signaling mechanisms, with the class I BRAFV600E mutation occurring most frequently in colorectal cancer. Functional categorization of BRAF mutations in colorectal cancer demonstrates distinct mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway signaling. On the basis of recent clinical trials, current standard-of-care therapies for patients with BRAFV600E-mutated metastatic colorectal cancer include first-line cytotoxic chemotherapy plus bevacizumab and subsequent therapy with the BRAF inhibitor encorafenib and antiepidermal growth factor receptor antibody cetuximab. Treatment regimens currently under exploration in BRAFV600E-mutant metastatic colorectal cancer include combinatorial options of various pathway-targeted therapies, cytotoxic chemotherapy, and/or immune checkpoint blockade, among others. Circumvention of adaptive and acquired resistance to BRAF-targeted therapies is a significant challenge to be overcome in BRAF-mutated advanced colorectal cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (
Figures
References
-
- Weber CK, Slupsky JR, Kalmes HA, et al. Active Ras induces heterodimerization of cRaf and BRaf. Cancer Res. 2001;61:3595–3598. - PubMed
-
- Dougherty MK, Muller J, Ritt DA, et al. Regulation of Raf-1 by direct feedback phosphorylation. Mol Cell. 2005;17:215–224. - PubMed
-
- Douville E, Downward J. EGF induced SOS phosphorylation in PC12 cells involves P90 RSK-2. Oncogene. 1997;15:373–383. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

