Ablation of the miRNA cluster 24 in cartilage and osteoblasts impairs bone remodeling
- PMID: 35650319
- PMCID: PMC9160244
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-13231-z
Ablation of the miRNA cluster 24 in cartilage and osteoblasts impairs bone remodeling
Abstract
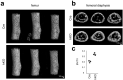
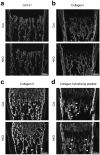
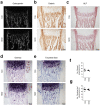
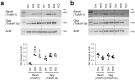
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) post-transcriptionally regulate cartilage and bone development and function, however, only few miRNAs have been described to play a role for cartilage to bone transition in vivo. Previously, we showed that cartilage-specific deletion of the Mirc24 cluster in newborn male mice leads to impaired growth plate cartilage development due to increased RAF/MEK/ERK signaling and affects the stability of the cartilage extracellular matrix on account of decreased SOX6 and SOX9 and increased MMP13 levels. Here, we studied how Mirc24 cluster inactivation in cartilage and osteoblasts leads to an increased bone density associated with defects in collagen remodeling in trabecular bone. No changes in osteoblast distribution were observed, whereas the number of osteoclasts was reduced and TRAP activity in osteoclasts decreased. Surprisingly, an increased level of cluster-encoded miR-322 or miR-503 raises Rankl gene expression and inactivation of the cluster in chondrocytes reduces Rankl expression. These results suggest that the Mirc24 cluster regulates Rankl expression in chondrocytes at the chondro-osseous border, where the cluster is mainly expressed to modulate osteoclast formation, bone remodeling and bone integrity.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ablation of the miRNA Cluster 24 Has Profound Effects on Extracellular Matrix Protein Abundance in Cartilage.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 9;21(11):4112. doi: 10.3390/ijms21114112. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32526967 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of beta catenin in hypertrophic growth plate chondrocytes impairs trabecular bone formation.Bone. 2013 Jul;55(1):102-12. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2013.03.019. Epub 2013 Apr 6. Bone. 2013. PMID: 23567158
-
The mineral dissolution function of osteoclasts is dispensable for hypertrophic cartilage degradation during long bone development and growth.Dev Biol. 2014 Sep 1;393(1):57-70. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2014.06.020. Epub 2014 Jun 30. Dev Biol. 2014. PMID: 24992711
-
Matrix metalloproteinase-13: A special focus on its regulation by signaling cascades and microRNAs in bone.Int J Biol Macromol. 2018 Apr 1;109:338-349. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.12.091. Epub 2017 Dec 19. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018. PMID: 29273522 Review.
-
MicroRNA biogenesis and regulation of bone remodeling.Arthritis Res Ther. 2011 May 27;13(3):220. doi: 10.1186/ar3325. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011. PMID: 21635717 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
MiR-322-5p is involved in regulating chondrocyte proliferation and differentiation in offspring's growth plate of maternal gestational diabetes.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 29;14(1):20136. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-69523-z. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39209899 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

