Extrafollicular Plasmablasts Present in the Acute Phase of Infections Express High Levels of PD-L1 and Are Able to Limit T Cell Response
- PMID: 35651611
- PMCID: PMC9149371
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.828734
Extrafollicular Plasmablasts Present in the Acute Phase of Infections Express High Levels of PD-L1 and Are Able to Limit T Cell Response
Abstract
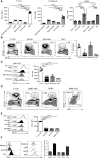
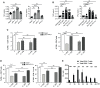
During infections with protozoan parasites or some viruses, T cell immunosuppression is generated simultaneously with a high B cell activation. It has been described that, as well as producing antibodies, plasmablasts, the differentiation product of activated B cells, can condition the development of protective immunity in infections. Here, we show that, in T. cruzi infection, all the plasmablasts detected during the acute phase of the infection had higher surface expression of PD-L1 than other mononuclear cells. PD-L1hi plasmablasts were induced in vivo in a BCR-specific manner and required help from Bcl-6+CD4+T cells. PD-L1hi expression was not a characteristic of all antibody-secreting cells since plasma cells found during the chronic phase of infection expressed PD-L1 but at lower levels. PD-L1hi plasmablasts were also present in mice infected with Plasmodium or with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus, but not in mice with autoimmune disorders or immunized with T cell-dependent antigens. In vitro experiments showed that PD-L1hi plasmablasts suppressed the T cell response, partially via PD-L1. Thus, this study reveals that extrafollicular PD-L1hi plasmablasts, whose peaks of response precede the peak of germinal center response, may have a modulatory function in infections, thus influencing T cell response.
Keywords: B cell; LCMV; PD-L1; Plasmodium; Trypanosoma cruzi; immunosuppression; microorganism evasion; plasmablasts/plasma cells.
Copyright © 2022 Serrán, Vernengo, Almada, Beccaria, Gazzoni, Canete, Roco, Boari, Ramello, Wehrens, Cai, Zuniga, Montes, Cockburn, Rodriguez, Vinuesa and Gruppi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Morán-Utrera Y, López-Monteon A, Rosales-Encina JL, Méndez-Bolaina E, Ramos-Ligonio A. Trypanosoma Cruzi SSP4 Amastigote Protein Induces Expression of Immunoregulatory and Immunosuppressive Molecules in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells. J Trop Med (2012) 2012:1–10. doi: 10.1155/2012/829139 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Poncini CV, Giménez G, Pontillo CA, Alba-Soto CD, de Isola ELD, Piazzón I, et al. . Central Role of Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase and Toll-Like Receptor 4 in IL-10 Production in Regulatory Dendritic Cells Induced by Trypanosoma Cruzi. Mol Immunol (2010) 47(11–12):1981–8. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2010.04.016 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

