The hexokinase Gene Family in Cotton: Genome-Wide Characterization and Bioinformatics Analysis
- PMID: 35651774
- PMCID: PMC9149573
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2022.882587
The hexokinase Gene Family in Cotton: Genome-Wide Characterization and Bioinformatics Analysis
Abstract
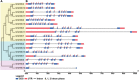
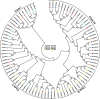
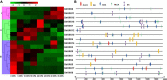
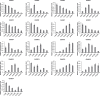
Hexokinase (HXK) is involved in hexose phosphorylation, sugar sensing, and signal transduction, all of which regulate plant growth and adaptation to stresses. Gossypium hirsutum L. is one of the most important fiber crops in the world, however, little is known about the HXKs gene family in G. hirsutum L. We identified 17 GhHXKs from the allotetraploid G. hirsutum L. genome (AADD). G. raimondii (DD) and G. arboreum (AA) are the diploid progenitors of G. hirsutum L. and contributed equally to the At_genome and Dt_genome GhHXKs genes. The chromosomal locations and exon-intron structures of GhHXK genes among cotton species are conservative. Phylogenetic analysis grouped the HXK proteins into four and three groups based on whether they were monocotyledons and dicotyledons, respectively. Duplication event analysis demonstrated that HXKs in G. hirsutum L. primarily originated from segmental duplication, which prior to diploid hybridization. Experiments of qRT-PCR, transcriptome and promoter cis-elements demonstrated that GhHXKs' promoters have auxin and GA responsive elements that are highly expressed in the fiber initiation and elongation stages, while the promoters contain ABA-, MeJA-, and SA-responsive elements that are highly expressed during the synthesis of the secondary cell wall. We performed a comprehensive analysis of the GhHXK gene family is a vital fiber crop, which lays the foundation for future studies assessing its role in fiber development.
Keywords: Gossypium hirsutum; expression pattern; hexokinase; sequence analysis; the evolutionary.
Copyright © 2022 Dou, Li, Wang, Li, Xiao and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The reviewer JG declared a shared affiliation with the author XZ to the handling editor at the time of review.
Figures







References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

