Supervised Computer-Aided Diagnosis (CAD) Methods for Classifying Alzheimer's Disease-Based Neurodegenerative Disorders
- PMID: 35651921
- PMCID: PMC9150998
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/9092289
Supervised Computer-Aided Diagnosis (CAD) Methods for Classifying Alzheimer's Disease-Based Neurodegenerative Disorders
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Supervised Computer-Aided Diagnosis (CAD) Methods for Classifying Alzheimer's Disease-Based Neurodegenerative Disorders.Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Dec 13;2023:9759262. doi: 10.1155/2023/9759262. eCollection 2023. Comput Math Methods Med. 2023. PMID: 38124963 Free PMC article.
Abstract
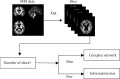
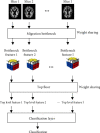
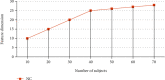
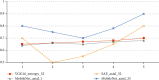
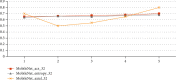
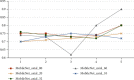
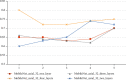
Alzheimer's disease is incurable at the moment. If it can be appropriately diagnosed, the correct treatment can postpone the patient's illness. To aid in the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease and to minimize the time and expense associated with manual diagnosis, a machine learning technique is employed, and a transfer learning method based on 3D MRI data is proposed. Machine learning algorithms can dramatically reduce the time and effort required for human treatment of Alzheimer's disease. This approach extracts bottleneck features from the M-Net migration network and then adds a top layer to supervised training to further decrease the dimensionality and delete portions. As a consequence, the transfer network presented in this study has several advantages in terms of computational efficiency and training time savings when used as a machine learning approach for AD-assisted diagnosis. Finally, the properties of all subject slices are combined and trained in the classification layer, completing the categorization of Alzheimer's disease symptoms and standard control. The results show that this strategy has a 1.5 percentage point better classification accuracy than the one that relies exclusively on VGG16 to extract bottleneck features. This strategy could cut the time it takes for the network to learn and improve its ability to classify things. The experiment shows that the method works by using data from OASIS. A typical transfer learning network's classification accuracy is about 8% better with this method than with a typical network, and it takes about 1/60 of the time with this method.
Copyright © 2022 Suneet Gupta et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Fuse H., Oishi K., Maikusa N., Fukami T., Initiative J. A. D. N. Detection of Alzheimer's disease with shape analysis of MRI images. 2018 Joint 10th International Conference on Soft Computing and Intelligent Systems (SCIS) and 19th International Symposium on Advanced Intelligent Systems (ISIS); 2018; Toyama, Japan. pp. 1031–1034. - DOI
-
- Patel R., Liu J., Chen K., Reiman E., Alexander G., Ye J. Sparse inverse covariance analysis of human brain for Alzheimer's disease study. 2009 ICME International Conference on Complex Medical Engineering; 2009; Tempe, AZ, USA. pp. 1–5. - DOI
-
- Guo X., Chen K., Chen Y., et al. A computational Monte Carlo simulation strategy to determine the temporal ordering of abnormal age onset among biomarkers of Alzheimers disease. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Computational Biology and Bioinformatics . 2021:p. 1. doi: 10.1109/TCBB.2021.3106939. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Li H., Fan Y. Early prediction of Alzheimer’s disease dementia based on baseline hippocampal MRI and 1-year follow-up cognitive measures using deep recurrent neural networks. 2019 IEEE 16th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2019); 2019; Venice, Italy. pp. 368–371. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

