TGF-β1 mediates pathologic changes of secondary lymphedema by promoting fibrosis and inflammation
- PMID: 35652284
- PMCID: PMC9160979
- DOI: 10.1002/ctm2.758
TGF-β1 mediates pathologic changes of secondary lymphedema by promoting fibrosis and inflammation
Abstract
Background: Secondary lymphedema is a common complication of cancer treatment, and previous studies have shown that the expression of transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-β1), a pro-fibrotic and anti-lymphangiogenic growth factor, is increased in this disease. Inhibition of TGF-β1 decreases the severity of the disease in mouse models; however, the mechanisms that regulate this improvement remain unknown.
Methods: Expression of TGF-β1 and extracellular matrix molecules (ECM) was assessed in biopsy specimens from patients with unilateral breast cancer-related lymphedema (BCRL). The effects of TGF-β1 inhibition using neutralizing antibodies or a topical formulation of pirfenidone (PFD) were analyzed in mouse models of lymphedema. We also assessed the direct effects of TGF-β1 on lymphatic endothelial cells (LECs) using transgenic mice that expressed a dominant-negative TGF-β receptor selectively on LECs (LECDN-RII ).
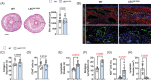
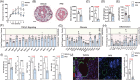
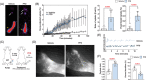
Results: The expression of TGF-β1 and ECM molecules is significantly increased in BCRL skin biopsies. Inhibition of TGF-β1 in mouse models of lymphedema using neutralizing antibodies or with topical PFD decreased ECM deposition, increased the formation of collateral lymphatics, and inhibited infiltration of T cells. In vitro studies showed that TGF-β1 in lymphedematous tissues increases fibroblast, lymphatic endothelial cell (LEC), and lymphatic smooth muscle cell stiffness. Knockdown of TGF-β1 responsiveness in LECDN-RII resulted in increased lymphangiogenesis and collateral lymphatic formation; however, ECM deposition and fibrosis persisted, and the severity of lymphedema was indistinguishable from controls.
Conclusions: Our results show that TGF-β1 is an essential regulator of ECM deposition in secondary lymphedema and that inhibition of this response is a promising means of treating lymphedema.
Keywords: TGF-β; fibrosis; inflammation; pirfenidone.
© 2022 The Authors. Clinical and Translational Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Shanghai Institute of Clinical Bioinformatics.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Mehrara is an advisor to PureTech Corporation and recipient of an investigator‐initiated award from PureTech and Regeneron Corp.
Figures
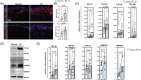
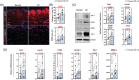
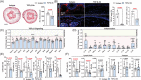
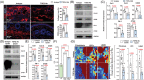
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
