Fibrinogen and Factor XIII in Venous Thrombosis and Thrombus Stability
- PMID: 35652333
- PMCID: PMC9339521
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.122.317164
Fibrinogen and Factor XIII in Venous Thrombosis and Thrombus Stability
Abstract
As the third most common vascular disease, venous thromboembolism is associated with significant mortality and morbidity. Pathogenesis underlying venous thrombosis is still not fully understood. Accumulating data suggest fibrin network structure and factor XIII-mediated crosslinking are major determinants of venous thrombus mass, composition, and stability. Understanding the cellular and molecular mechanisms mediating fibrin(ogen) and factor XIII production and function and their ability to influence venous thrombosis and resolution may inspire new anticoagulant strategies that target these proteins to reduce or prevent venous thrombosis in certain at-risk patients. This article summarizes fibrinogen and factor XIII biology and current knowledge of their function during venous thromboembolism.
Keywords: anticoagulant; fibrinogen; hemostasis; red blood cell; venous thrombosis.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST DISCLOSURE
Neither of the authors have relevant potential conflict of interest.
Figures

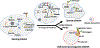
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

