Gene-rich X chromosomes implicate intragenomic conflict in the evolution of bizarre genetic systems
- PMID: 35653559
- PMCID: PMC9191650
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2122580119
Gene-rich X chromosomes implicate intragenomic conflict in the evolution of bizarre genetic systems
Abstract
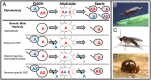
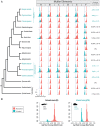
Haplodiploidy and paternal genome elimination (HD/PGE) are common in invertebrates, having evolved at least two dozen times, all from male heterogamety (i.e., systems with X chromosomes). However, why X chromosomes are important for the evolution of HD/PGE remains debated. The Haploid Viability Hypothesis posits that X-linked genes promote the evolution of male haploidy by facilitating purging recessive deleterious mutations. The Intragenomic Conflict Hypothesis holds that conflict between genes drives genetic system turnover; under this model, X-linked genes could promote the evolution of male haploidy due to conflicts with autosomes over sex ratios and genetic transmission. We studied lineages where we can distinguish these hypotheses: species with germline PGE that retain an XX/X0 sex determination system (gPGE+X). Because evolving PGE in these cases involves changes in transmission without increases in male hemizygosity, a high degree of X linkage in these systems is predicted by the Intragenomic Conflict Hypothesis but not the Haploid Viability Hypothesis. To quantify the degree of X linkage, we sequenced and compared 7 gPGE+X species’ genomes with 11 related species with typical XX/XY or XX/X0 genetic systems, representing three transitions to gPGE. We find highly increased X linkage in both modern and ancestral genomes of gPGE+X species compared to non-gPGE relatives and recover a significant positive correlation between percent X linkage and the evolution of gPGE. These empirical results substantiate longstanding proposals for a role for intragenomic conflict in the evolution of genetic systems such as HD/PGE.
Keywords: genomic conflict; haplodiploidy; insects; sex chromosomes; sex determination.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures

References
-
- Hamilton W. D., Extraordinary sex ratios. A sex-ratio theory for sex linkage and inbreeding has new implications in cytogenetics and entomology. Science 156, 477–488 (1967). - PubMed
-
- Hartl D. L., Brown S. W., The origin of male haploid genetic systems and their expected sex ratio. Theor. Popul. Biol. 1, 165–190 (1970). - PubMed
-
- Bull J. J., An advantage for the evolution of male haploidy and systems with similar genetic transmission. Heredity 43, 361–381 (1979).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

