Neuronal NLRP3 is a parkin substrate that drives neurodegeneration in Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 35654037
- PMCID: PMC9357148
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2022.05.009
Neuronal NLRP3 is a parkin substrate that drives neurodegeneration in Parkinson's disease
Abstract
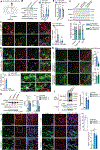
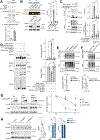
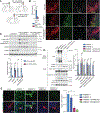
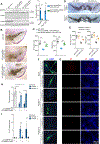
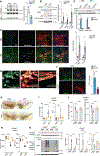
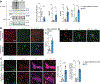
Parkinson's disease (PD) is mediated, in part, by intraneuronal accumulation of α-synuclein aggregates andsubsequent death of dopamine (DA) neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc). Microglial hyperactivation of the NOD-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome has been well-documented in various neurodegenerative diseases, including PD. We show here that loss of parkin activity in mouse and human DA neurons results in spontaneous neuronal NLRP3 inflammasome assembly, leading to DA neuron death. Parkin normally inhibits inflammasome priming by ubiquitinating and targeting NLRP3 for proteasomal degradation. Loss of parkin activity also contributes to the assembly of an active NLRP3 inflammasome complex via mitochondrial-derived reactive oxygen species (mitoROS) generation through the accumulation of another parkin ubiquitination substrate, ZNF746/PARIS. Inhibition of neuronal NLRP3 inflammasome assembly prevents degeneration of DA neurons in familial and sporadic PD models. Strategies aimed at limiting neuronal NLRP3 inflammasome activation hold promise as a disease-modifying therapy for PD.
Keywords: Caspase-1; NLRP3; PARIS; Parkinson’s disease; ZNF746; inflammasome; neurodegeneration; parkin; ubiquitination.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The value of patents owned by Valted could be affected by the study described in this article. Drs. T.D. and V.D. are founders of Valted and hold an ownership equity interest in the company. This arrangement has been reviewed and approved by the Johns Hopkins University in accordance with its conflict-of-interest policies.
Figures

Comment in
-
Taking the parkin brakes off of neuronal NLRP3 drives inflammasome activation and neurodegeneration in Parkinson's disease.Neuron. 2022 Aug 3;110(15):2356-2358. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2022.06.015. Neuron. 2022. PMID: 35926449
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

