A pro-metastatic tRNA fragment drives Nucleolin oligomerization and stabilization of its bound metabolic mRNAs
- PMID: 35654044
- PMCID: PMC9444141
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2022.05.008
A pro-metastatic tRNA fragment drives Nucleolin oligomerization and stabilization of its bound metabolic mRNAs
Abstract
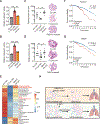
Stress-induced cleavage of transfer RNAs (tRNAs) into tRNA-derived fragments (tRFs) occurs across organisms from yeast to humans; yet, its mechanistic underpinnings and pathological consequences remain poorly defined. Small RNA profiling revealed increased abundance of a cysteine tRNA fragment (5'-tRFCys) during breast cancer metastatic progression. 5'-tRFCys was required for efficient breast cancer metastatic lung colonization and cancer cell survival. We identified Nucleolin as the direct binding partner of 5'-tRFCys. 5'-tRFCys promoted the oligomerization of Nucleolin and its bound metabolic transcripts Mthfd1l and Pafah1b1 into a higher-order transcript stabilizing ribonucleoprotein complex, which protected these transcripts from exonucleolytic degradation. Consistent with this, Mthfd1l and Pafah1b1 mediated pro-metastatic and metabolic effects downstream of 5'-tRFCys-impacting folate, one-carbon, and phosphatidylcholine metabolism. Our findings reveal that a tRF can promote oligomerization of an RNA-binding protein into a transcript stabilizing ribonucleoprotein complex, thereby driving specific metabolic pathways underlying cancer progression.
Keywords: Mthfd1l; Pafah1b1; breast cancer; metastasis; nucleolin; oligomerization; post-transcriptional; tRF; tRNA fragment; transcript stability.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests S.F.T. is a cofounder, shareholder, and member of the scientific advisory board of Inspirna.
Figures
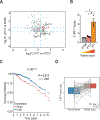
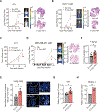
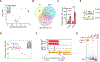
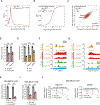
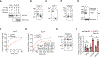
Comment in
-
A tRF nucleator for Nucleolin in cancer metastasis.Mol Cell. 2022 Jul 21;82(14):2536-2538. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2022.06.025. Mol Cell. 2022. PMID: 35868253
References
-
- Abdelmohsen K, Tominaga K, Lee EK, Srikantan S, Kang MJ, Kim MM, Selimyan R, Martindale JL, Yang X, Carrier F, et al. (2011). Enhanced translation by Nucleolin via G-rich elements in coding and non-coding regions of target mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res 39, 8513–8530. 10.1093/nar/gkr488. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

