Discovery of the cyclotide caripe 11 as a ligand of the cholecystokinin-2 receptor
- PMID: 35654807
- PMCID: PMC9163038
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-13142-z
Discovery of the cyclotide caripe 11 as a ligand of the cholecystokinin-2 receptor
Abstract
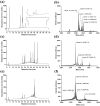
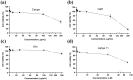
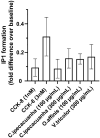
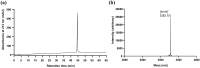
The cholecystokinin-2 receptor (CCK2R) is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that is expressed in peripheral tissues and the central nervous system and constitutes a promising target for drug development in several diseases, such as gastrointestinal cancer. The search for ligands of this receptor over the past years mainly resulted in the discovery of a set of distinct synthetic small molecule chemicals. Here, we carried out a pharmacological screening of cyclotide-containing plant extracts using HEK293 cells transiently-expressing mouse CCK2R, and inositol phosphate (IP1) production as a readout. Our data demonstrated that cyclotide-enriched plant extracts from Oldenlandia affinis, Viola tricolor and Carapichea ipecacuanha activate the CCK2R as measured by the production of IP1. These findings prompted the isolation of a representative cyclotide, namely caripe 11 from C. ipecacuanha for detailed pharmacological analysis. Caripe 11 is a partial agonist of the CCK2R (Emax = 71%) with a moderate potency of 8.5 µM, in comparison to the endogenous full agonist cholecystokinin-8 (CCK-8; EC50 = 11.5 nM). The partial agonism of caripe 11 is further characterized by an increase on basal activity (at low concentrations) and a dextral-shift of the potency of CCK-8 (at higher concentrations) following its co-incubation with the cyclotide. Therefore, cyclotides such as caripe 11 may be explored in the future for the design and development of cyclotide-based ligands or imaging probes targeting the CCK2R and related peptide GPCRs.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

