HER2 G776S mutation promotes oncogenic potential in colorectal cancer cells when accompanied by loss of APC function
- PMID: 35654814
- PMCID: PMC9163061
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-13189-y
HER2 G776S mutation promotes oncogenic potential in colorectal cancer cells when accompanied by loss of APC function
Abstract
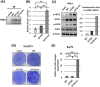
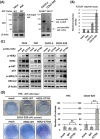
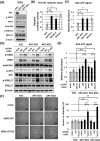
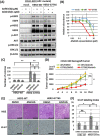
Clinical cancer genome sequencing detects oncogenic variants that are potential targets for cancer treatment, but it also detects variants of unknown significance. These variants may interact with each other to influence tumor pathophysiology, however, such interactions have not been fully elucidated. Additionally, the effect of target therapy for those variants also unclarified. In this study, we investigated the biological functions of a HER2 mutation (G776S mutation) of unknown pathological significance, which was detected together with APC mutation by cancer genome sequencing of samples from a colorectal cancer (CRC) patient. Transfection of the HER2 G776S mutation alone slightly increased the kinase activity and phosphorylation of HER2 protein, but did not activate HER2 downstream signaling or alter the cell phenotype. On the other hand, the HER2 G776S mutation was shown to have strong oncogenic potential when loss of APC function was accompanied. We revealed that loss of APC function increased Wnt pathway activity but also increased RAS-GTP, which increased ERK phosphorylation triggered by HER2 G776S transfection. In addition, afatinib, a pan-HER tyrosine kinase inhibitor, suppressed tumor growth in xenografts derived from HER2 G776S-transfected CRC cells. These findings suggest that this HER2 mutation in CRC may be a potential therapeutic target.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Oncogenic KRAS signalling promotes the Wnt/β-catenin pathway through LRP6 in colorectal cancer.Oncogene. 2015 Sep 17;34(38):4914-27. doi: 10.1038/onc.2014.416. Epub 2014 Dec 15. Oncogene. 2015. PMID: 25500543 Free PMC article.
-
PHLPP is a negative regulator of RAF1, which reduces colorectal cancer cell motility and prevents tumor progression in mice.Gastroenterology. 2014 May;146(5):1301-12.e1-10. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2014.02.003. Epub 2014 Feb 11. Gastroenterology. 2014. PMID: 24530606 Free PMC article.
-
TRIB3 Interacts With β-Catenin and TCF4 to Increase Stem Cell Features of Colorectal Cancer Stem Cells and Tumorigenesis.Gastroenterology. 2019 Feb;156(3):708-721.e15. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.10.031. Epub 2018 Oct 24. Gastroenterology. 2019. PMID: 30365932
-
Molecular biology of colorectal cancer.Curr Probl Cancer. 1997 Sep-Oct;21(5):233-300. doi: 10.1016/s0147-0272(97)80003-7. Curr Probl Cancer. 1997. PMID: 9438104 Review.
-
Colorectal cancer: a multipathway disease.Crit Rev Oncog. 2006 Dec;12(3-4):273-87. doi: 10.1615/critrevoncog.v12.i3-4.50. Crit Rev Oncog. 2006. PMID: 17425506 Review.
Cited by
-
Semi-Synthetic Dihydrotestosterone Derivatives Modulate Inherent Multidrug Resistance and Sensitize Colon Cancer Cells to Chemotherapy.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Feb 9;15(2):584. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15020584. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36839907 Free PMC article.
-
HER2 phosphorylation induced by TGF-β promotes mammary morphogenesis and breast cancer progression.J Cell Biol. 2024 Apr 1;223(4):e202307138. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202307138. Epub 2024 Feb 26. J Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38407425 Free PMC article.
-
The Wnt/β-Catenin Inhibitor HC-1 Suppresses Liver Fibrosis by Inhibiting Activated Hepatic Stellate Cells and Inducing Matrix Metalloproteinase-1.Yonago Acta Med. 2025 May 17;68(2):131-143. doi: 10.33160/yam.2025.05.009. eCollection 2025 May. Yonago Acta Med. 2025. PMID: 40432742 Free PMC article.
-
HER2-targeted therapy in colorectal cancer: a comprehensive review.Clin Transl Oncol. 2025 Sep;27(9):3607-3624. doi: 10.1007/s12094-025-03887-0. Epub 2025 Mar 14. Clin Transl Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40087250 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jiang J, Greulich H, Janne PA, Sellers WR, Meyerson M, Griffin JD. Epidermal growth factor-independent transformation of Ba/F3 cells with cancer-derived epidermal growth factor receptor mutants induces gefitinib-sensitive cell cycle progression. Cancer Res. 2005;65(19):8968–8974. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-1829. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

