Hypoxia-induced inhibin promotes tumor growth and vascular permeability in ovarian cancers
- PMID: 35654828
- PMCID: PMC9163327
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-022-03495-6
Hypoxia-induced inhibin promotes tumor growth and vascular permeability in ovarian cancers
Abstract
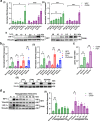
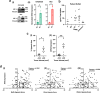
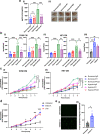
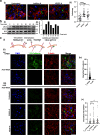
Hypoxia, a driver of tumor growth and metastasis, regulates angiogenic pathways that are targets for vessel normalization and ovarian cancer management. However, toxicities and resistance to anti-angiogenics can limit their use making identification of new targets vital. Inhibin, a heteromeric TGFβ ligand, is a contextual regulator of tumor progression acting as an early tumor suppressor, yet also an established biomarker for ovarian cancers. Here, we find that hypoxia increases inhibin levels in ovarian cancer cell lines, xenograft tumors, and patients. Inhibin is regulated primarily through HIF-1, shifting the balance under hypoxia from activins to inhibins. Hypoxia regulated inhibin promotes tumor growth, endothelial cell invasion and permeability. Targeting inhibin in vivo through knockdown and anti-inhibin strategies robustly reduces permeability in vivo and alters the balance of pro and anti-angiogenic mechanisms resulting in vascular normalization. Mechanistically, inhibin regulates permeability by increasing VE-cadherin internalization via ACVRL1 and CD105, a receptor complex that we find to be stabilized directly by inhibin. Our findings demonstrate direct roles for inhibins in vascular normalization via TGF-β receptors providing new insights into the therapeutic significance of inhibins as a strategy to normalize the tumor vasculature in ovarian cancer.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

