YAP inhibits ERα and ER+ breast cancer growth by disrupting a TEAD-ERα signaling axis
- PMID: 35654829
- PMCID: PMC9163075
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-30831-5
YAP inhibits ERα and ER+ breast cancer growth by disrupting a TEAD-ERα signaling axis
Abstract
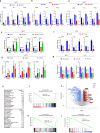
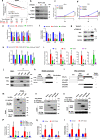
Hippo signaling restricts tissue growth by inhibiting the transcriptional effector YAP. Here we uncover a role of Hippo signaling and a tumor suppressor function of YAP in estrogen receptor positive (ER+) breast cancer. We find that inhibition of Hippo/MST1/2 or activation of YAP blocks the ERα transcriptional program and ER+ breast cancer growth. Mechanistically, the Hippo pathway transcription factor TEAD physically interacts with ERα to increase its promoter/enhancer occupancy whereas YAP inhibits ERα/TEAD interaction, decreases ERα occupancy on its target promoters/enhancers, and promotes ERα degradation by the proteasome. Furthermore, YAP inhibits hormone-independent transcription of ERα gene (ESR1). Consistently, high levels of YAP correlate with good prognosis of ER+ breast cancer patients. Finally, we find that pharmacological inhibition of Hippo/MST1/2 impeded tumor growth driven by hormone therapy resistant ERα mutants, suggesting that targeting the Hippo-YAP-TEAD signaling axis could be a potential therapeutical strategy to overcome endocrine therapy resistance conferred by ERα mutants.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

