Ki-67 proliferation index to further stratify invasive breast cancer molecular subtypes: Northern African comparative cohort-study with external TCGA-BRCA and METABRIC validation
- PMID: 35655690
- PMCID: PMC9120749
- DOI: 10.11604/pamj.2022.41.170.31239
Ki-67 proliferation index to further stratify invasive breast cancer molecular subtypes: Northern African comparative cohort-study with external TCGA-BRCA and METABRIC validation
Abstract
Introduction: breast cancer (BC) is a malignancy with very high incidence and mortality in Africa, especially in Western Africa, where more than 25 thousand deaths are registered every year. Not all BC have the same prognosis, and being able to personalize treatment and predict aggressiveness is of crucial importance. The purpose of our study is to explore further subdivisions associated with prognosis, beyond breast cancer molecular classification that is routinely established in pathology departments.
Methods: we conducted a 5-year retrospective cohort study on 1266 invasive BC of Moroccan patients, collected at the Pathology Department of Ibn-Rochd University Hospital in Casablanca, and followed at King Mohammed VI National Centre for the Treatment of Cancers. We elaborated an Estimation-Maximization Clustering, based on the main BC biomarkers: Ki-67, HER2, estrogen and progesterone receptors, evaluated by immunohistochemistry. Two independent datasets (TCGA-BRCA and Metabric) were also analyzed to assess the external reproducibility of the results.
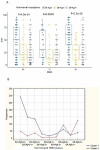
Results: each molecular subgroup could be partitioned into two further subdivisions: Cluster1, with average Ki-67 of 16.26% (±11.9) across all molecular subgroups and higher frequency within luminal BC, and Cluster2, with average Ki-67 of 68.8%(±18) across all molecular subgroups and higher frequency in HER2 as well as in triple-negative BC. Overall survival of the two Clusters was significantly different, with 5-year rates of 52 and 37 months for Custer1 and Cluster2, respectively (p=0.000001). Moreover, mortality rates within the same molecular subgroup, especially in luminal B HER2-, varied remarkably depending on Cluster membership (6% for C1 and 18% for C2 after 1 year of follow-up). Two different algorithms to evaluate the prognostic importance, variable selection using random forests (VSURF) and Minimal depth, ranked the subdivision proposed as one of the 4 most influential features being able to predict patient survival better than several histoprognostic features, both in the Moroccan and in the external datasets.
Conclusion: our results highlight a new refinement of the BC molecular classification and provide a simple and improved way to classify tumors that could be applied in low to middle-income countries. This is the first study of its kind addressed in an African context.
Keywords: Ki-67; clustering; estrogen; immunohistochemistry; progesterone; prognosis.
Copyright: Laila Akhouayri et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Geographic differences in the distribution of molecular subtypes of breast cancer in Brazil.BMC Womens Health. 2014 Aug 29;14:102. doi: 10.1186/1472-6874-14-102. BMC Womens Health. 2014. PMID: 25174527 Free PMC article.
-
The regrouping of Luminal B (HER2 negative), a better discriminator of outcome and recurrence score.Cancer Med. 2023 Feb;12(3):2493-2504. doi: 10.1002/cam4.5089. Epub 2022 Jul 31. Cancer Med. 2023. PMID: 35909232 Free PMC article.
-
A comparative study of Ki-67 antigen expression between luminal A and triple-negative subtypes of breast cancer.Med Oncol. 2017 Sep;34(9):156. doi: 10.1007/s12032-017-1019-x. Epub 2017 Aug 5. Med Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28780646
-
Impact of molecular subtypes classification concordance between preoperative core needle biopsy and surgical specimen on early breast cancer management: Single-institution experience and review of published literature.Eur J Surg Oncol. 2017 Apr;43(4):642-648. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2016.10.025. Epub 2016 Nov 17. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2017. PMID: 27889196 Review.
-
Ki67 and lymphocytes in the pretherapeutic core biopsy of primary invasive breast cancer: positive markers of therapy response prediction and superior survival.Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig. 2017 Sep 22;32(2):/j/hmbci.2017.32.issue-2/hmbci-2017-0022/hmbci-2017-0022.xml. doi: 10.1515/hmbci-2017-0022. Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig. 2017. PMID: 28937963 Review.
Cited by
-
Correlation Analysis of Ultrasound Elastography Score with Invasive Breast Cancer and Biological Prognostic Factors.Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2022 Jul 4;2022:1174541. doi: 10.1155/2022/1174541. eCollection 2022. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2022. Retraction in: Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2023 Jul 19;2023:9871968. doi: 10.1155/2023/9871968. PMID: 35873667 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
-
- World Health Organization The global cancer observatory. Globocan. 2020. Accessed August 7 2021.
-
- The foundation lalla salma cancer prevention and treatment Detection guide of early breast and cervical cancer. Accessed August 7 2021.
-
- Registre des Cancer de la Région du Grand Casablanca Cancer register of greater Casablanca region for 2008-2012. Accessed on September 6 2021.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous