Isolable fluorinated triphenylmethyl cation salts of [HCB11Cl11]-: demonstration of remarkable hydride affinity
- PMID: 35655874
- PMCID: PMC9067617
- DOI: 10.1039/d1sc05936j
Isolable fluorinated triphenylmethyl cation salts of [HCB11Cl11]-: demonstration of remarkable hydride affinity
Abstract
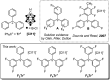
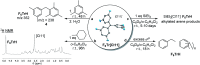
Significantly fluorinated triarylmethyl cations have long attracted attention as potentially accessible highly reactive carbocations, but their isolation in a convenient form has proved elusive. We show that abstraction of chloride with a cationic silylium reagent leads to the facile formation of di-, tetra-, and hexafluorinated trityl cations, which could be isolated as analytically pure salts with the [HCB11Cl11]- counterion and are compatible with (halo)arene solvents. The F6Tr+ cation carrying six meta-F substituents was computationally predicted to possess up to 20% higher hydride affinity than the parent triphenylmethyl cation Tr+. We report that indeed F6Tr+ displays reactivity unmatched by Tr+. F6Tr+ at ambient temperature abstracts hydrides from the C-H bonds in tetraethylsilane, mesitylene, methylcyclohexane, and catalyzes Friedel-Crafts alkylation of arenes with ethylene, while Tr+ does none of these.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures