Efficacy and Safety of Prostatic Artery Embolization in the Treatment of High Risk Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia and its Influence on Postoperative Life Quality of Patients
- PMID: 35656089
- PMCID: PMC9152163
- DOI: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.905394
Efficacy and Safety of Prostatic Artery Embolization in the Treatment of High Risk Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia and its Influence on Postoperative Life Quality of Patients
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the efficacy, safety and postoperative quality of life of high risk benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) patients treated with prostatic artery embolization.
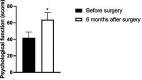
Methods: 34 patients with high-risk BPH were selectedfrom January 2020 to June 2021 in our hospital. All patients were treated with prostatic artery embolization. The changes of international prostate symptom score (IPSS), prostate volume (PV), remaining urine (RU), maximum urine flow rate (Qmax), quality of life scale -74(GQOLI-74), time to sleep without disturbance (HUS) judgment, self-rating anxiety scale (SAS) score and self-rating depression scale (SDS) were compared before operation, 1 month and 6 months after operation.
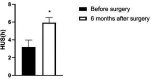
Results: Prostatic artery embolization was successful in all 34 patients, including unilateral embolization in 15 patients and bilateral embolization in 19 patients. No severe complications occurred in the postoperative patients. The IPSS, PV and RU levels of the patient one month and six months after surgery were lower than those before surgery, while the Qmax level was higher than that before surgery. Besides, the IPSS, PV and RU levels six months after surgery were significantly lower than those one month after surgery, and the Qmax level was significantly higher than that one month after surgery (p < 0.05). The GQOLI-74 score six months after surgery was significantly higher than that before surgery (p < 0.05). The HUS of the patient six months after surgery was significantly increased, and the SAS and SDS scores were significantly decreased as compared with those before surgery (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: For high-risk patients with BPH, prostate embolization is an effective and safe method, which can significantly improve the quality of life of patients after surgery and has good application prospects.
Keywords: benign prostatic hyperplasia; high risk; prostatic artery; prostatic artery embolization; quality of life.
Copyright © 2022 Wang, Chen, Liu, Xiao, Qian and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


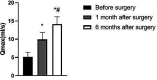
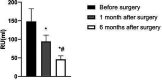
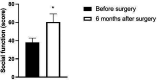

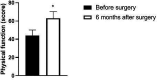

References
-
- Meng Q, Li J, Li M, Qiu R. Evaluation of efficacy and safety of improved transurethral plasma kinetic enucleation of the prostate in high-risk patients with benign prosta tic hyperplasia and coronary artery disease. J Int Med Res. (2021) 49:3000605211060890. 10.1177/03000605211060890 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhang ZY, Zhao MJ, Hong BA, Ma LL, Jin YH, Zeng XT, et al. [Transurethral bipolar plasmakinetic prostatectomy for benign prostatic hyperplasia in high-risk and senior patients in China: a systematic re view and meta-analysis]. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. (2019) 99:778–82. 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2019.10.015 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

