Skeletal Muscle Metabolic Alternation Develops Sarcopenia
- PMID: 35656108
- PMCID: PMC9116905
- DOI: 10.14336/AD.2021.1107
Skeletal Muscle Metabolic Alternation Develops Sarcopenia
Abstract
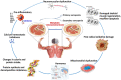
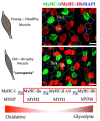
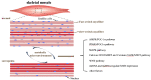
Sarcopenia is a new type of senile syndrome with progressive skeletal muscle mass loss with age, accompanied by decreased muscle strength and/or muscle function. Sarcopenia poses a serious threat to the health of the elderly and increases the burden of family and society. The underlying pathophysiological mechanisms of sarcopenia are still unclear. Recent studies have shown that changes of skeletal muscle metabolism are the risk factors for sarcopenia. Furthermore, the importance of the skeletal muscle metabolic microenvironment in regulating satellite cells (SCs) is gaining significant attention. Skeletal muscle metabolism has intrinsic relationship with the regulation of skeletal muscle mass and regeneration. This review is to discuss recent findings regarding skeletal muscle metabolic alternation and the development of sarcopenia, hoping to contribute better understanding and treatment of sarcopenia.
Keywords: Sarcopenia; metabolic alternation; regeneration; signaling pathways.
Copyright: © 2022 Yang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Boncompagni S, D'Amelio L, Fulle S, Fanò G, Protasi F (2006). Progressive Disorganization of the Excitation-Contraction Coupling Apparatus in Aging Human Skeletal Muscle as Revealed by Electron Microscopy: A Possible Role in the Decline of Muscle Performance. Journals of Gerontology, 61:995. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
