Nanoencapsulation of n-butanol extract of Symphytum kurdicum and Symphytum asperrimum: Focus on phytochemical analysis, anti-oxidant and antibacterial activity
- PMID: 35656178
- PMCID: PMC9148405
- DOI: 10.22038/IJBMS.2022.62032.13760
Nanoencapsulation of n-butanol extract of Symphytum kurdicum and Symphytum asperrimum: Focus on phytochemical analysis, anti-oxidant and antibacterial activity
Abstract
Objectives: The current study's objectives were to obtain different extracts and essential oils of Symphytum kurdicum and Symphytum asperrimum and to determine the chemical composition, as well as to evaluate free radical scavenging activity (IC50) and minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC), and the effect of liposomal formulation on antimicrobial properties.
Materials and methods: Air-dried powdered aerial parts of S. kurdicum and S. asperrimum were used. The antioxidant and antibacterial properties, essential oil compositions, total phenol, and flavonoid contents of different fractions were determined by DPPH test, disk diffusion assay, gas chromatography-mass spectrometry, Folin-ciocalteu reagent, and colorimetric assay method, respectively. The film hydration method was used to fabricate nanoparticles.
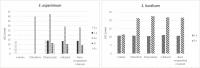
Results: GC-MS analysis indicated that hexafarnesyl acetone was a major essential oil component. n-butanol and ethyl acetate extracts of S. kurdicum had the highest anti-oxidant activity. Extracts of both plants showed antimicrobial activity. The extracts' maximum inhibition zones against Staphylococcus epidermidis were established. A particle size analyzer detected the formulation size of 140 nm. The optimum formulation of liposomes contains the ratio of 75 mg lecithin, 25 mg cholesterol, and 50 mg herbal extract. Despite the nanoparticles' appropriate particle size, the liposomal extract's antimicrobial effect was lower than that of the free form.
Conclusion: Our findings demonstrated that extracts have significant antibacterial and anti-oxidant activities, attributed to their bioactive constituents.
Keywords: Anti-oxidants; Boraginaceae; Comfrey; Flavonoids; Liposome; Microbial sensitivity tests; Nanoparticle.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bilal M, Rasheed T, Iqbal HMN, Hu H, Wang W, Zhang X. Macromolecular agents with antimicrobial potentialities: A drive to combat antimicrobial resistance. Int J Biol Macromol. 2017;103:554–574. - PubMed
-
- Sirbu R, Gabriela S, Tomescu A, Ionescu A, Cadar E. Evaluation of antioxidant and antimicrobial activity in relation to total phenolic content of green algae from black sea. Revista de Chimie. 2019;70:1197–1203.
-
- Mohan A, Alzubaidy A. A comparative systematic study of the genus Symphytum l (Boraginaceae) with new first record of the species Symphytum tuberosum l. From iraQ. Plant Arch. 2018;18:2068–2076.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous