Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria: An Etiopathogenic Study
- PMID: 35656272
- PMCID: PMC9154155
- DOI: 10.4103/ijd.ijd_851_21
Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria: An Etiopathogenic Study
Abstract
Importance: Exact etiopathogenesis of chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU) remains elusive. Infections, pseudoallergens, autoimmunity, and contact sensitization are various postulated factors. Few studies are available measuring cytokine levels in CSU.
Objectives: The aim was to study various etiological factors of CSU and levels of IL-6 and IFN-ϒ in cases and controls, and correlation between various etiologies with the levels of the abovementioned interleukins in the cases.
Design: Case-control study performed over 2 years with no follow-up of the participants.
Setting: It was a referral-center-based study.
Participants: Sixty patients of CSU and equal age and sex-matched healthy controls were recruited on the basis of convenience sampling.
Exposures: Biochemical and hematological investigations with hepatitis serology, thyroid function tests, anti-thyroid antibodies, and levels IL-6 and IFN-ϒ were performed in all cases and controls. All cases were subjected to ASST. Cases with all above negative tests were patch-tested with Indian standard series. Urticaria activity score (UAS7) was calculated for all the cases and repeated in patients with positive etiological factor after 3 weeks (improvement after allergen or drug avoidance, treatment of infection).
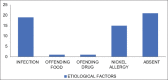
Outcomes: To study the various etiological factors (food, infection, autoimmunity, autoreactivity, and contact sensitization) and the levels of IL-6 and IFN- γ in patients of chronic spontaneous urticaria.
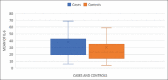
Results: Etiology was ascertained in 75% of patients (autoimmunity: 50%, contact sensitization: 21.67%, food and drug allergy: 1.67% each). Mean values of the interleukins and anti-thyroid antibodies were significantly higher in cases versus controls. Levels of IFN-ϒ were significantly elevated in patients with higher UAS7 scores.
Conclusion: Antithyroid antibodies, ASST, and patch testing are important tools and should be considered in patients of CSU after a thorough history and history-based workup. Elevated levels of IL-6 and IFN- ϒ in cases suggest that both Th1 and Th2 type of immune responses are implicated in pathogenesis of CSU.
Keywords: ASST; IFN-gamma; IL-6; UAS7; chronic spontaneous urticaria.
Copyright: © 2022 Indian Journal of Dermatology.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Grattan CE, Sabroe RA, Greaves MW. Chronic urticaria. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;46:645–57. - PubMed
-
- Kaplan AP. Chronic urticaria: Pathogenesis and treatment. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004;114:465–74. - PubMed
-
- Atwa MA, Emara AS, Youssef N, Bayoumy NM. Serum concentration of IL-17, IL-23 and TNF-α among patients with chronic spontaneous urticaria: Association with disease activity and autologous serum skin test. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2014;28:469–74. - PubMed
-
- Zuberbier T, Aberer W, Asero R, Abdul Latiff AH, Baker D, Ballmer-Weber B, et al. The EAACI/GA2LEN/EDF/WAO guideline for the definition, classification, diagnosis and management of urticaria. Allergy. 2018;73:1393–414. - PubMed
-
- Greaves MW. Chronic idiopathic urticaria. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003;3:363–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
