Diabetes Fact Sheet in Korea 2021
- PMID: 35656565
- PMCID: PMC9171160
- DOI: 10.4093/dmj.2022.0106
Diabetes Fact Sheet in Korea 2021
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to investigate the prevalence and management of diabetes mellitus, risk-factor control, and comorbidities among Korean adults.
Methods: We conducted a cross-sectional analysis of data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey to assess the prevalence, treatment, risk factors, comorbidities, and self-management behaviors of diabetes mellitus from 2019 to 2020. We also analyzed data from the Korean National Health Insurance Service to evaluate the use of antidiabetic medications in people with diabetes mellitus from 2002 through 2018.
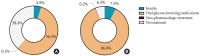
Results: Among Korean adults aged 30 years or older, the estimated prevalence of diabetes mellitus was 16.7% in 2020. From 2019 through 2020, 65.8% of adults with diabetes mellitus were aware of the disease and treated with antidiabetic medications. The percentage of adults with diabetes mellitus who achieved glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) <6.5% was 24.5% despite the increased use of new antidiabetic medications. We found that adults with diabetes mellitus who achieved all three goals of HbA1c <6.5%, blood pressure (BP) <140/85 mm Hg, and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol <100 mg/dL were 9.7%. The percentage of self-management behaviors was lower in men than women. Excess energy intake was observed in 16.7% of adults with diabetes mellitus.
Conclusion: The prevalence of diabetes mellitus among Korean adults remained high. Only 9.7% of adults with diabetes mellitus achieved all glycemic, BP, and lipid controls from 2019 to 2020. Continuous evaluation of national diabetes statistics and a national effort to increase awareness of diabetes mellitus and improve comprehensive diabetes care are needed.
Keywords: Comorbidity; Diabetes mellitus; Disease management; Health behavior; Prevalence; Republic of Korea; Risk factors.
Conflict of interest statement
Seung-Hyun Ko has been executive editor of the
Figures


References
-
- International Diabetes Federation . IDF diabetes atlas. 10th ed. Brussels: IDF; 2021.
-
- Zheng Y, Ley SH, Hu FB. Global aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2018;14:88–98. - PubMed
-
- Korean Diabetes Association . Seoul: Korean Diabetes Association; 2018. Diabetes fact sheet in Korea, 2018.
-
- Korean Diabetes Association . Seoul: Korean Diabetes Association; 2020. Diabetes fact sheet in Korea, 2020.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

