Ischemic Postconditioning Attenuates Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion-Induced Acute Lung Injury by Regulating Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Mediated Apoptosis
- PMID: 35657304
- PMCID: PMC10010732
- DOI: 10.21470/1678-9741-2021-0043
Ischemic Postconditioning Attenuates Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion-Induced Acute Lung Injury by Regulating Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Mediated Apoptosis
Abstract
Objective: To explore the effect of ischemic postconditioning on myocardial ischemia-reperfusion-induced acute lung injury (ALI).
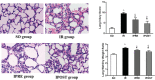
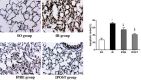
Methods: Forty adult male C57BL/6 mice were randomly divided into sham operation group (SO group), myocardial ischemia-reperfusion group (IR group), ischemic preconditioning group (IPRE group) and ischemic postconditioning group (IPOST group) (10 mice in each group). Anterior descending coronary artery was blocked for 60 min and then reperfused for 15 min to induce myocardial IR. For the IPRE group, 3 consecutive cycles of 5 min of occlusion and 5 minutes of reperfusion of the coronary arteries were performed before ischemia. For the IPOST group, 3 consecutive cycles of 5 min reperfusion and 5 minutes of occlusion of the coronary arteries were performed before reperfusion. Pathological changes of lung tissue, lung wet-to-dry (W/D) weight ratio, inflammatory factors, oxidative stress indicators, apoptosis of lung cells and endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS) protein were used to evaluate lung injury.
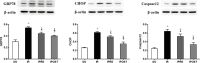
Results: After myocardial IR, lung injury worsened significantly, manifested by alveolar congestion, hemorrhage, structural destruction of alveolar septal thickening, and interstitial neutrophil infiltration. In addition, lung W/D ratio was increased, plasma inflammatory factors, including interleukin (IL)-6, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, and IL-17A, were increased, malondialdehyde (MDA) activity of lung tissue was increased, and superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity was decreased after myocardial IR. It was accompanied by the increased protein expression levels of ERS-related protein glucose regulatory protein 78 (GRP78), CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein (C/EBP) homologous protein (CHOP), and caspase-12, and the increased apoptotic indices of lung tissues.
Conclusion: IPOST can effectively improve myocardial IR-induced ALI by inhibiting ERS-induced apoptosis of alveolar epithelial cells.
Keywords: Acute Lung Injury; Alveolar Epithelial Cells; Apoptosis; Carrier Proteins; Coronary Vessels; Ischemia-Reperfusion; Ischemic Postconditioning.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
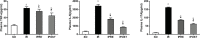
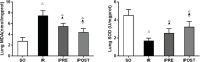
Similar articles
-
Immediate but not delayed postconditioning during reperfusion attenuates acute lung injury induced by intestinal ischemia/reperfusion in rats: comparison with ischemic preconditioning.J Surg Res. 2009 Nov;157(1):e55-62. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2008.11.843. Epub 2008 Dec 13. J Surg Res. 2009. PMID: 19345372
-
Effects of endomorphin-1 postconditioning on myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury and myocardial cell apoptosis in a rat model.Mol Med Rep. 2016 Oct;14(4):3992-8. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5695. Epub 2016 Aug 31. Mol Med Rep. 2016. PMID: 27600942
-
[Effects of excessive endoplasmic reticulum stress on lung ischemia/reperfusion induced myocardial injury in mice].Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2018 Jan 8;34(1):8-13. doi: 10.12047/j.cjap.5581.2018.003. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 29926651 Chinese.
-
Cardioprotection of pharmacological postconditioning on myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury.Life Sci. 2021 Jan 1;264:118628. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118628. Epub 2020 Oct 22. Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33131670 Review.
-
DJ-1: Potential target for treatment of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury.Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 Oct;179:117383. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.117383. Epub 2024 Sep 3. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 39232383 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of Natural Products through Inhibiting Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress on Attenuation of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024 May 17;18:1627-1650. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S388920. eCollection 2024. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024. PMID: 38774483 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
