ER-lysosome lipid transfer protein VPS13C/PARK23 prevents aberrant mtDNA-dependent STING signaling
- PMID: 35657605
- PMCID: PMC9170524
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.202106046
ER-lysosome lipid transfer protein VPS13C/PARK23 prevents aberrant mtDNA-dependent STING signaling
Abstract
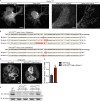
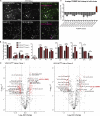
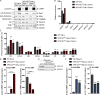
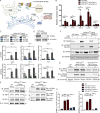
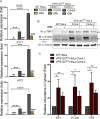
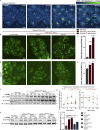
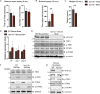
Mutations in VPS13C cause early-onset, autosomal recessive Parkinson's disease (PD). We have established that VPS13C encodes a lipid transfer protein localized to contact sites between the ER and late endosomes/lysosomes. In the current study, we demonstrate that depleting VPS13C in HeLa cells causes an accumulation of lysosomes with an altered lipid profile, including an accumulation of di-22:6-BMP, a biomarker of the PD-associated leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) G2019S mutation. In addition, the DNA-sensing cGAS-STING pathway, which was recently implicated in PD pathogenesis, is activated in these cells. This activation results from a combination of elevated mitochondrial DNA in the cytosol and a defect in the degradation of activated STING, a lysosome-dependent process. These results suggest a link between ER-lysosome lipid transfer and innate immune activation in a model human cell line and place VPS13C in pathways relevant to PD pathogenesis.
© 2022 Hancock-Cerutti et al.
Figures




References
-
- Alcalay, R.N., Hsieh F., Tengstrand E., Padmanabhan S., Baptista M., Kehoe C., Narayan S., Boehme A.K., and Merchant K.. 2020. Higher urine bis(Monoacylglycerol)Phosphate levels in LRRK2 G2019S mutation carriers: Implications for therapeutic development. Mov. Disord. 35:134–141. 10.1002/mds.27818 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

