Cross Talk Between Insulin and Glucagon Receptor Signaling in the Hepatocyte
- PMID: 35657690
- PMCID: PMC9450567
- DOI: 10.2337/dbi22-0002
Cross Talk Between Insulin and Glucagon Receptor Signaling in the Hepatocyte
Abstract
While the consumption of external energy (i.e., feeding) is essential to life, this action induces a temporary disturbance of homeostasis in an animal. A primary example of this effect is found in the regulation of glycemia. In the fasted state, stored energy is released to maintain physiological glycemic levels. Liver glycogen is liberated to glucose, glycerol and (glucogenic) amino acids are used to build new glucose molecules (i.e., gluconeogenesis), and fatty acids are oxidized to fuel long-term energetic demands. This regulation is driven primarily by the counterregulatory hormones epinephrine, growth hormone, cortisol, and glucagon. Conversely, feeding induces a rapid influx of diverse nutrients, including glucose, that disrupt homeostasis. Consistently, a host of hormonal and neural systems under the coordination of insulin are engaged in the transition from fasting to prandial states to reduce this disruption. The ultimate action of these systems is to appropriately store the newly acquired energy and to return to the homeostatic norm. Thus, at first glance it is tempting to assume that glucagon is solely antagonistic regarding the anabolic effects of insulin. We have been intrigued by the role of glucagon in the prandial transition and have attempted to delineate its role as beneficial or inhibitory to glycemic control. The following review highlights this long-known yet poorly understood hormone.
© 2022 by the American Diabetes Association.
Figures
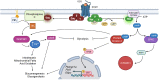
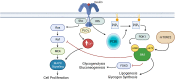
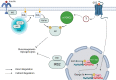
References
-
- Banting FG, Best CH. The internal secretions of the pancreas. J Lab Clin Med 1922;5:251–266
-
- Kimball CP, Murlin JR. Aqueous extracts of pancreas. III. Some precipitation reactions of insulin. J Biol Chem 1923;58:337–346
-
- Murlin JR, Clough HD, Gibbs CBF, Stokes AM. Aqueous extracts of the pancreas. I. Influence on the carbohydrate metabolism of depancreatized animals. J Biol Chem 1923;56:253–296
-
- Bürger M, Brandt W. Über das glukagon (die hyperglykämisierende substanz des pankreas). Z Gesamte Exp Med 1935;96:375
-
- Bürger M, Kramer H. Über den hepatischen angriffspunkt des insulins. Z Gesamte Exp Med 1929;65:487–497
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

