Phytochemical profiling and cellular antioxidant efficacy of different rice varieties in colorectal adenocarcinoma cells exposed to oxidative stress
- PMID: 35657911
- PMCID: PMC9165792
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0269403
Phytochemical profiling and cellular antioxidant efficacy of different rice varieties in colorectal adenocarcinoma cells exposed to oxidative stress
Abstract
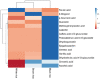
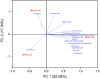
In the present study, white (Baegilmi), brown (hyunmi) and black (chalheugmi) Korean local rice varieties ethanol extracts were analyzed for in-vitro antioxidant assays (ABTS, FRAP and DPPH), cellular antioxidant activities (CAAs) and phenolic phytochemicals content. The highest antioxidant assays, phenolic, flavonoid and anthocyanins content were identified among the free fractions of black rice. Phenolic phytochemicals were detected and quantified using the ultra-high-performance liquid tandem chromatography quadrupole flight mass spectrometry (UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS2). Which indicated the richness of several phytochemicals like ascorbic acid, vanillic acid, p-coumaric acid, catechin, epigallocatechin and quercetin in black rice than in other rice samples. The cellular antioxidant activities (CAA) of black rice were found equivalent to that of ascorbic acid, the standard employed in the assay. The CAAs of free fractions were as follows: white rice < brown rice < black rice. These findings are significant for enhancing human health through increased consumption of black and brown rice in the development of functional food products.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

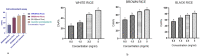
References
-
- Hathout HM, Sobhy HM, Abou-Ghanima S, El-Garawani IM. Ameliorative role of ascorbic acid on the oxidative stress and genotoxicity induced by acetamiprid in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Environmental Science and Pollution Research. 2021:1–13. - PubMed
-
- Fuentes J, de Camargo AC, Atala E, Gotteland M, Olea-Azar C, Speisky H. Quercetin Oxidation Metabolite Present in Onion Peel Protects Caco-2 Cells against the Oxidative Stress, NF-kB Activation, and Loss of Epithelial Barrier Function Induced by NSAIDs. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 2021;69(7):2157–67. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.0c07085 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

